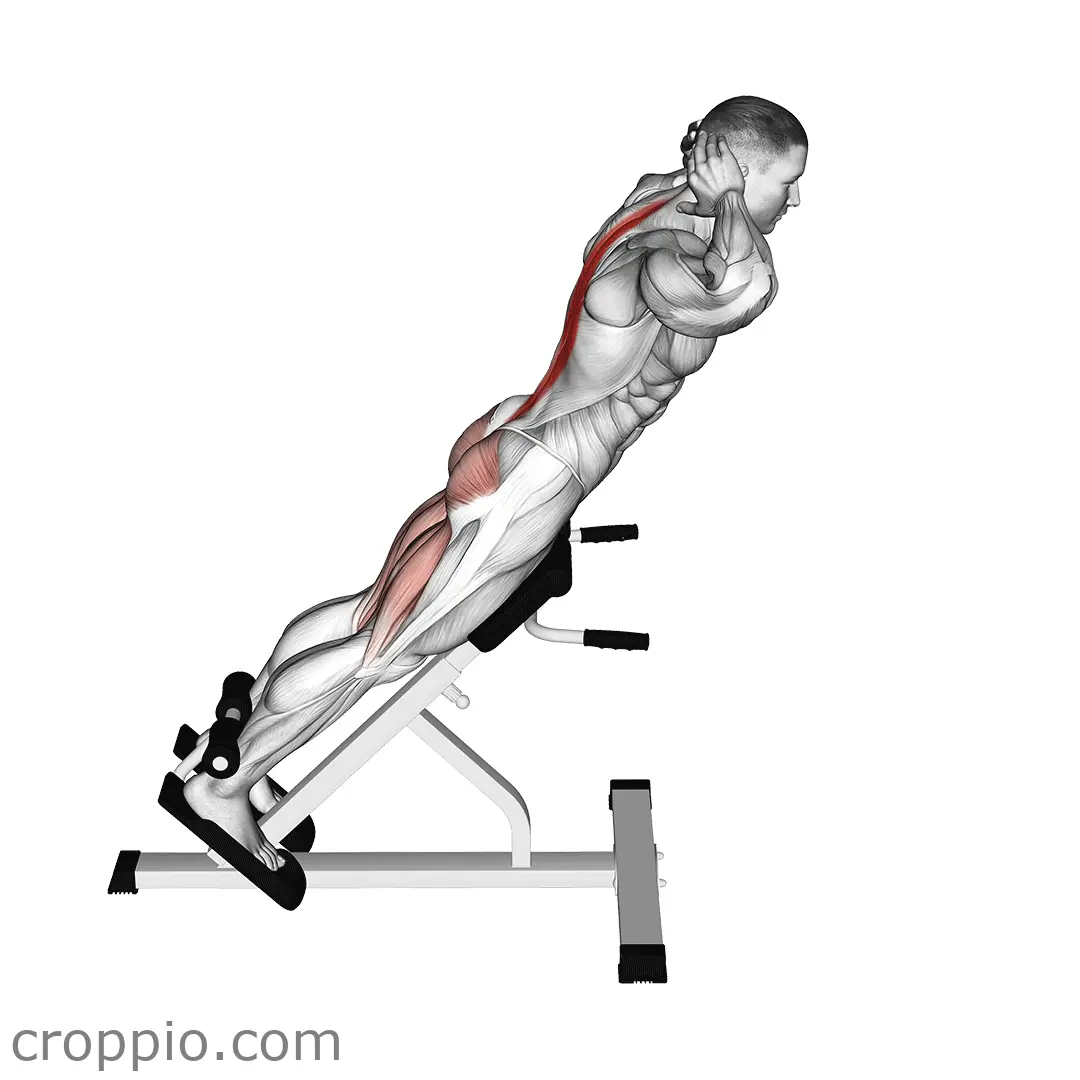
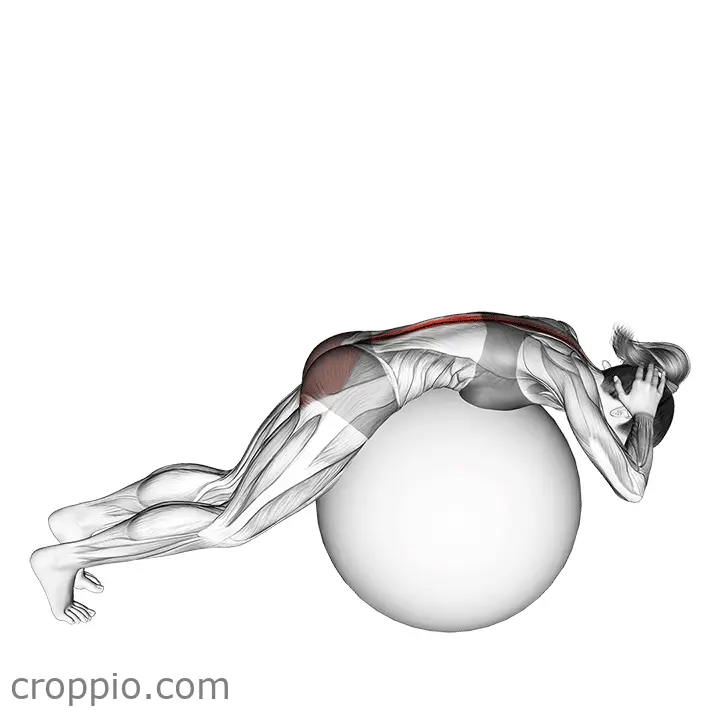
Lying Back Extension
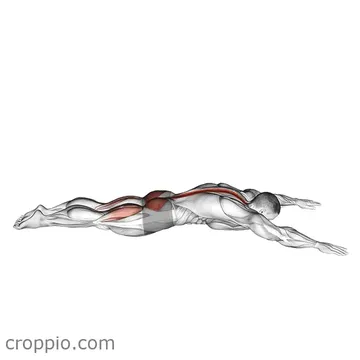
Latest Videos
No videos available.
Lying Back Extension Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
The lying back extension primarily targets the erector spinae, a group of muscles located alongside the spine that are essential for back extension and stabilization. In addition, this exercise engages the gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and lower back muscles, contributing to overall posterior chain development. Secondary involvement includes the core muscles, particularly the transverse abdominis, which helps support the lower back during the movement.
Top Mistakes
- Incorrect Neck Position: Allowing the head to lift excessively can strain the neck and lead to discomfort.
- Hyperextending the Back: Overextending the back during the exercise can cause injury; the movement should be controlled and limited to a natural extension.
- Lack of Core Engagement: Failing to engage the core might compromise stability and increase the risk of lower back strain.
Execution Tips
- Body Alignment: Lie face down on a flat surface or a back extension bench, ensuring your body is in a straight line from head to toe.
- Head Position: Keep your head in a neutral position, looking down rather than lifting it to avoid neck strain.
- Control the Movement: Lift your upper body by engaging your back muscles and maintaining a tight core. Avoid using momentum; focus on a slow and controlled contraction.
- Range of Motion: Lift to just above parallel to the ground to maximize muscle engagement while preventing hyperextension.
Workouts
The lying back extension can be a powerful addition to any strength training routine. Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, ensuring quality over quantity. This exercise can be effectively combined with complementary movements such as deadlifts or squats, which also target the posterior chain. Consider performing this exercise 2-3 times per week as part of a back-focused workout day or integrated within your overall routine to boost lower back and glute strength.
Conclusion
The lying back extension offers numerous benefits, including improved posture, greater lower back strength, and enhanced athletic performance. By effectively engaging the posterior chain, this exercise not only helps in injury prevention but also promotes overall core stability. Incorporating lying back extensions into your routine can lead to a stronger, more resilient back, crucial for daily activities and physical performance.