Reverse Hyperextension
Reverse Hyperextension Workouts
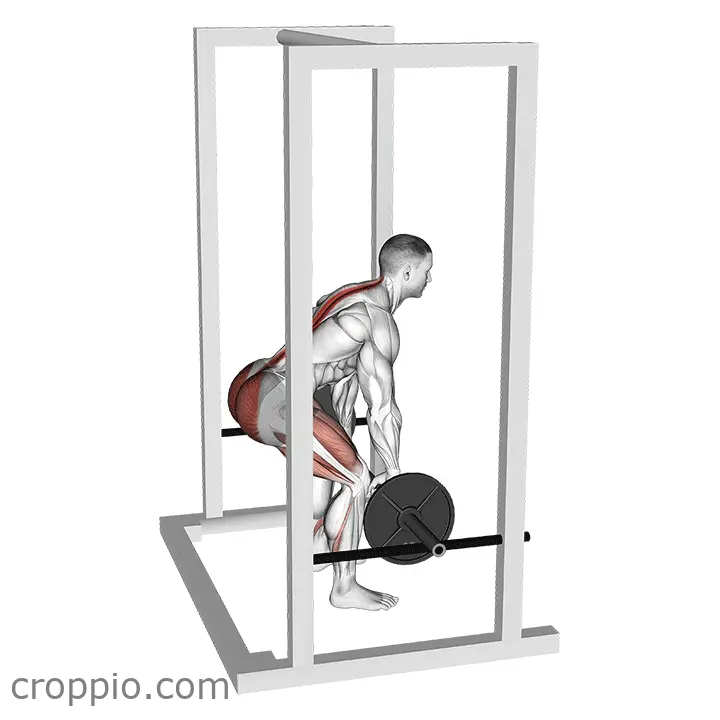
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
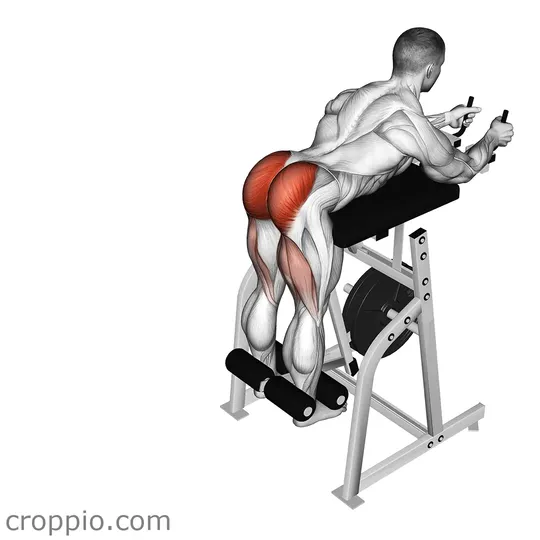
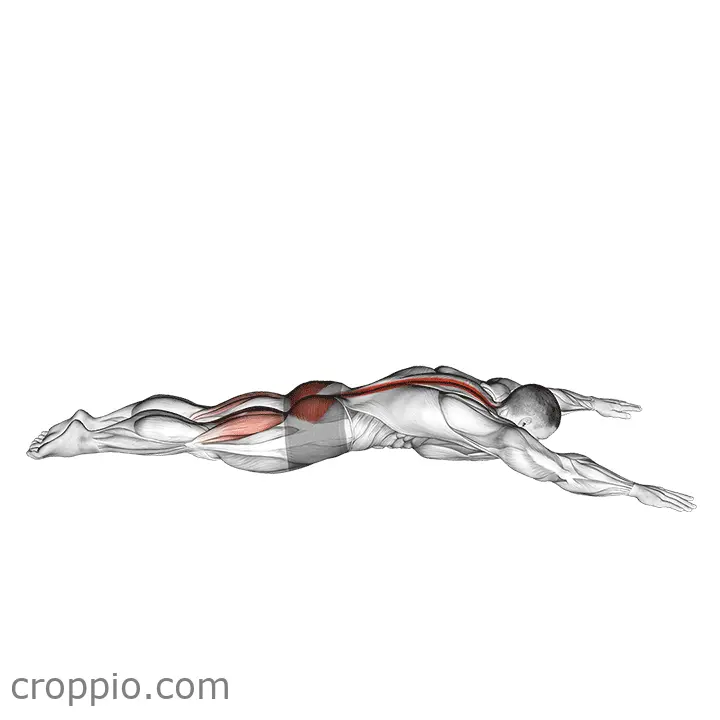
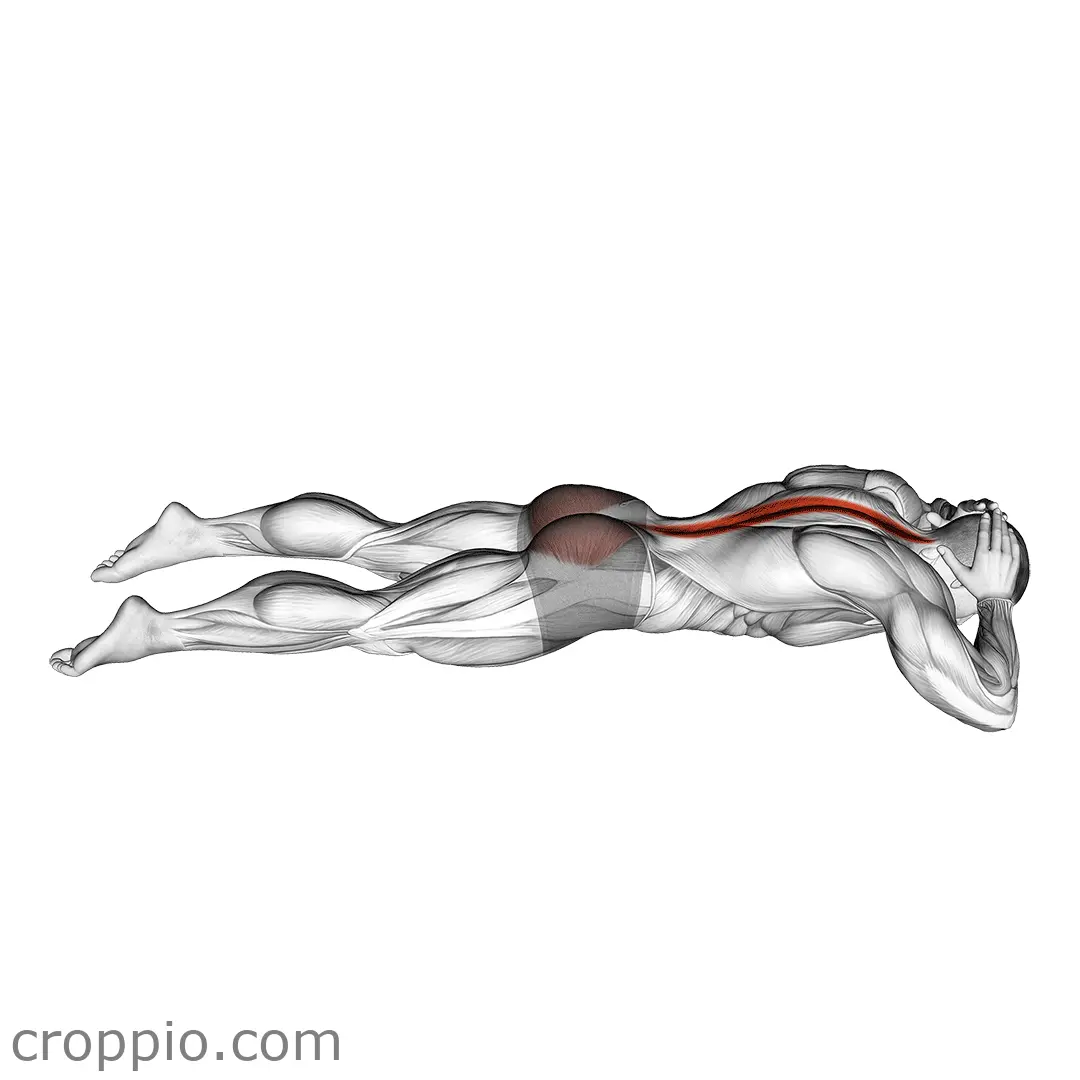
The reverse hyperextension exercise primarily targets the posterior chain, focusing mainly on the gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and lower back muscles, including the erector spinae. As you perform the movement, the gluteus maximus contracts to extend the hips, while the hamstrings assist in stabilizing the movement and facilitating the lifting of the legs. Secondary muscles involved include the core stabilizers, such as the abdominals and obliques, which work to maintain proper spinal alignment and balance throughout the exercise. Engaging these muscles not only helps to strengthen the lower body but also improves overall core stability.
Top Mistakes
- Incorrect hip position: Allowing the hips to rise excessively or sagging can lead to improper alignment.
- Overextension of the lower back: Lifting the legs too high can place undue stress on the lumbar spine.
- Lack of control: Rushing through the movement can lead to improper form and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Neglecting engagement of core: Failing to engage the core can lead to instability and potential injury.
Execution Tips
- Begin by setting up on a reverse hyperextension machine or a bench, ensuring your hips are at the edge and your legs hang freely.
- Anchor your upper body with your arms or straps to maintain stability. Keep your torso neutral throughout the movement.
- Engage your core while slowly lifting your legs towards the ceiling—focus on using your glutes and hamstrings to control the movement.
- Aim to raise your legs to about parallel to the ground, avoiding any overextension that can strain the lower back.
- Lower your legs back down in a controlled manner without letting them swing, maintaining tension in the working muscle groups.
Workouts
The reverse hyperextension can be effectively incorporated into various workout routines. For optimal results, performing 3 to 4 sets of 10 to 15 repetitions is recommended. This exercise can complement lower body workouts or focused posterior chain training, making it a great addition to sessions that include squats, deadlifts, or leg curls. It can also be paired with movements like bridges or lunges to enhance muscle activation and overall leg strength.
Conclusion
The reverse hyperextension exercise is a highly beneficial addition to any fitness regimen, specifically for those looking to strengthen the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back. By enhancing strength and stability in the posterior chain, it promotes better posture, reduces the risk of injury, and improves athletic performance. Integrating this exercise into your routine can lead to significant gains in lower body strength and overall functional fitness.