Floor Back Extensions
Latest Videos
Floor Back Extensions Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
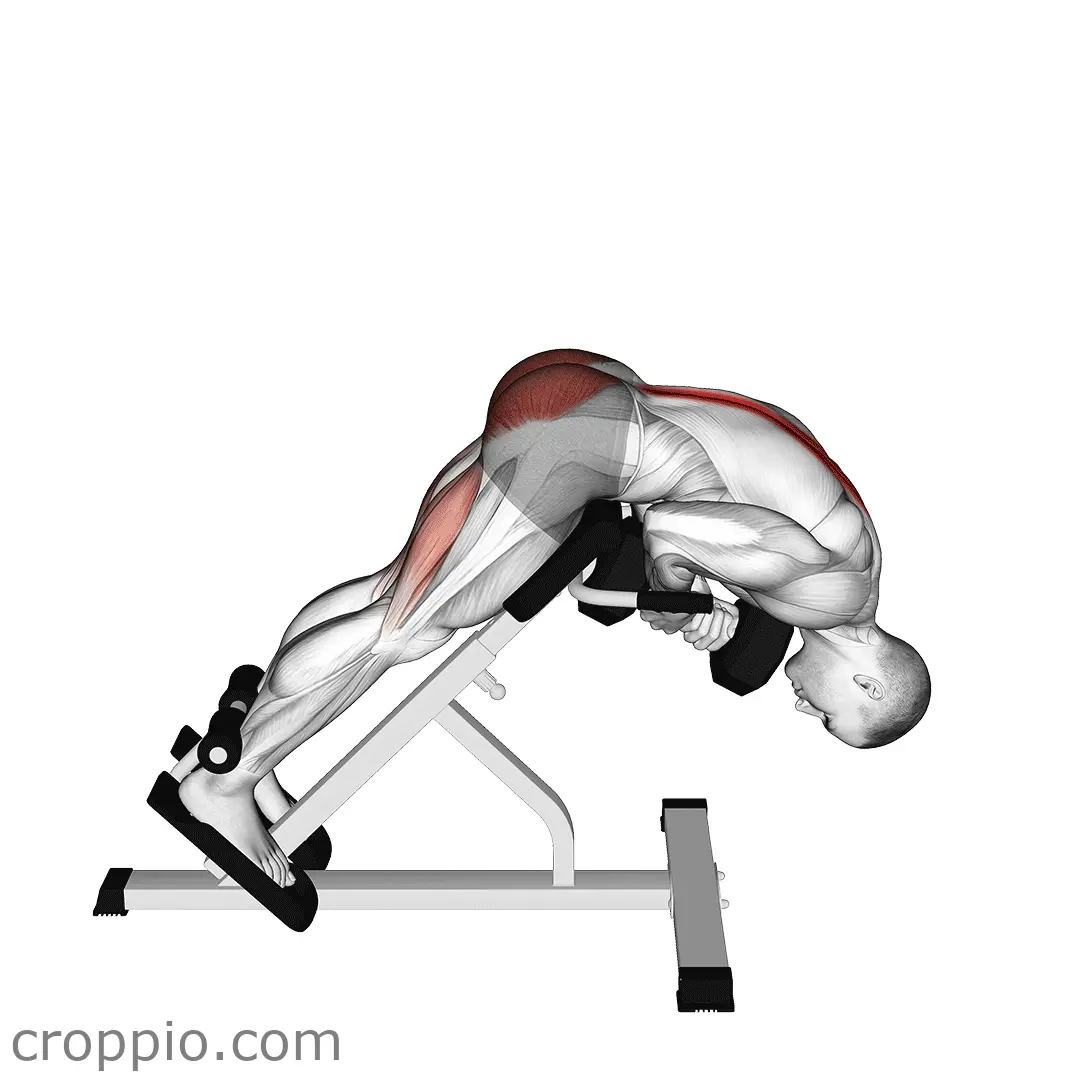
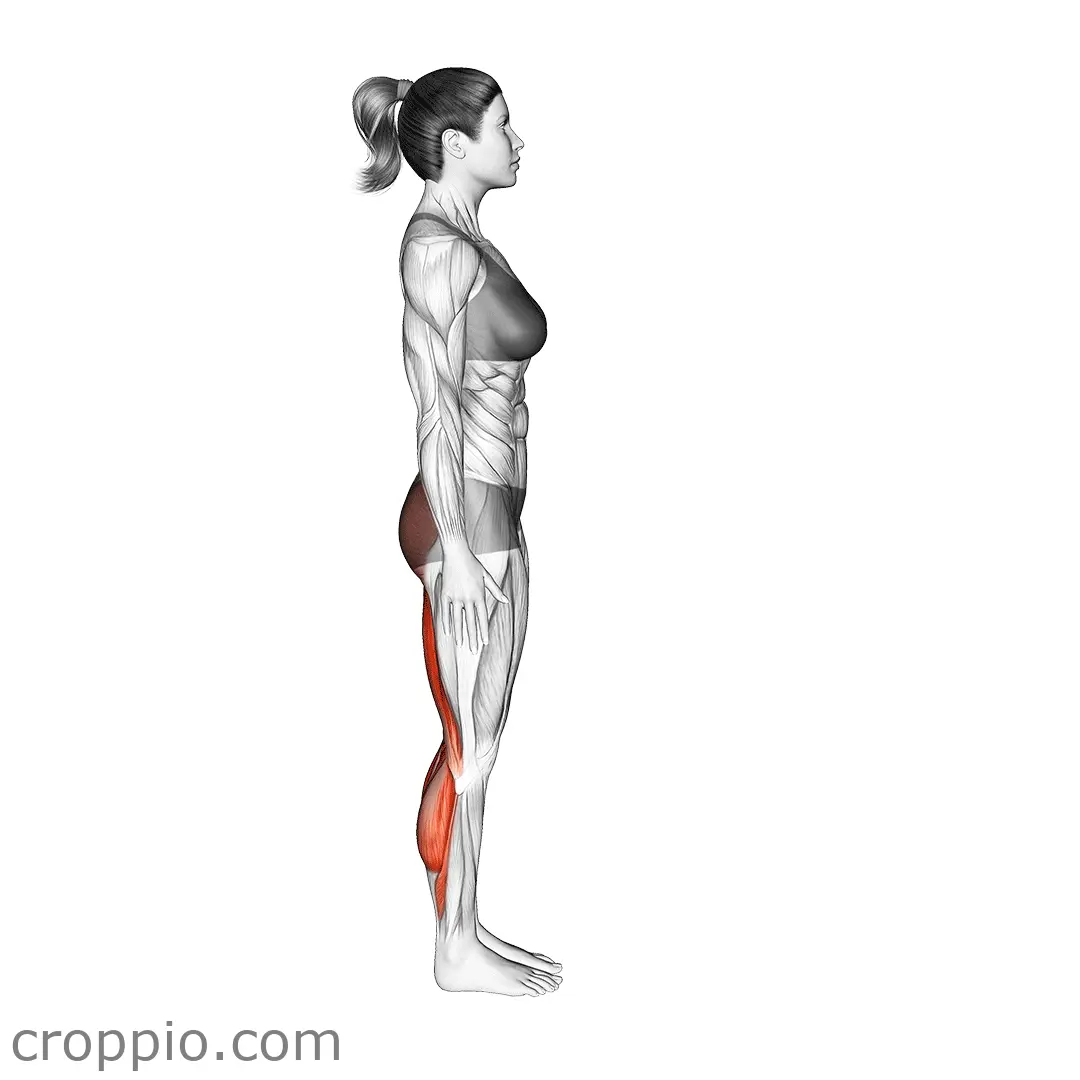
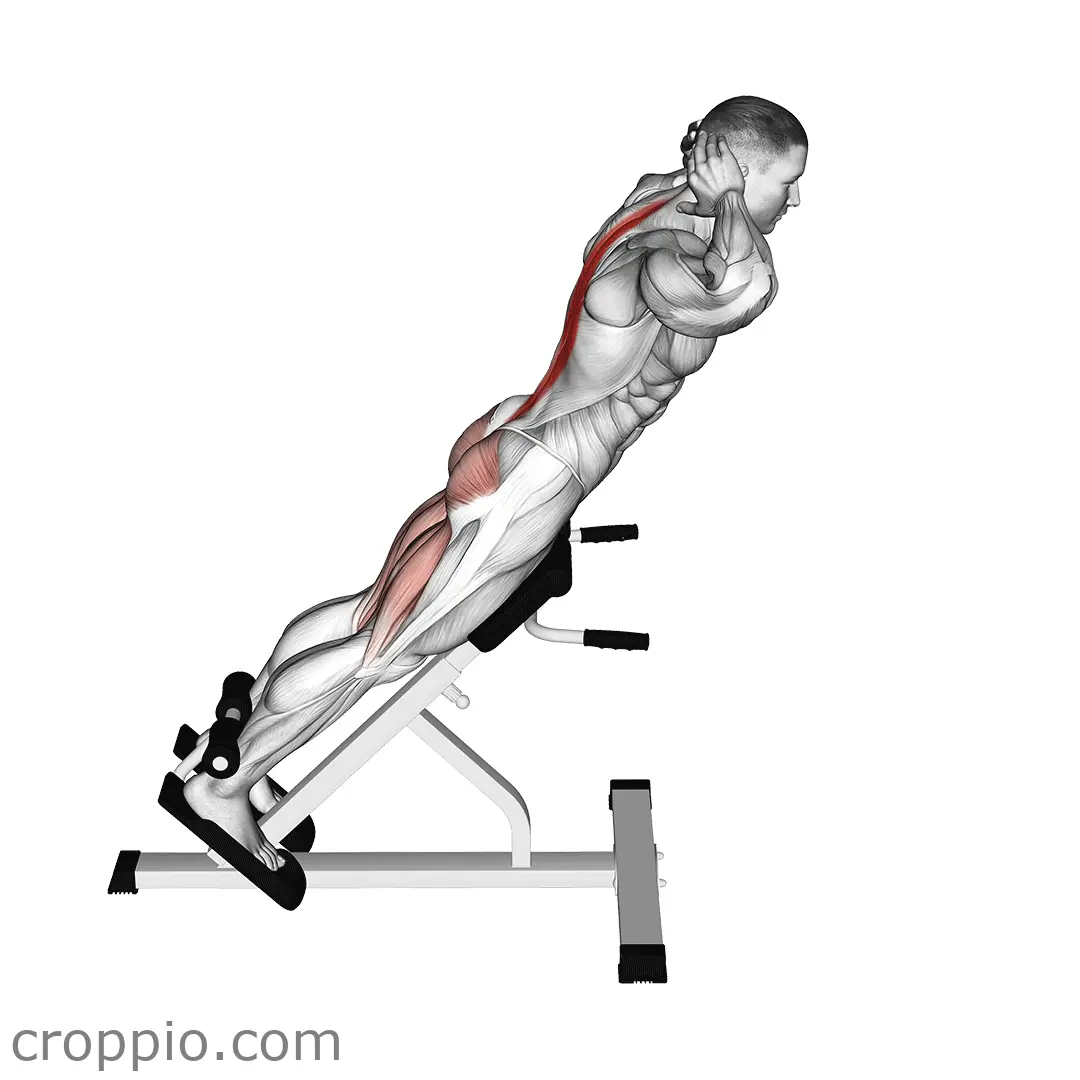
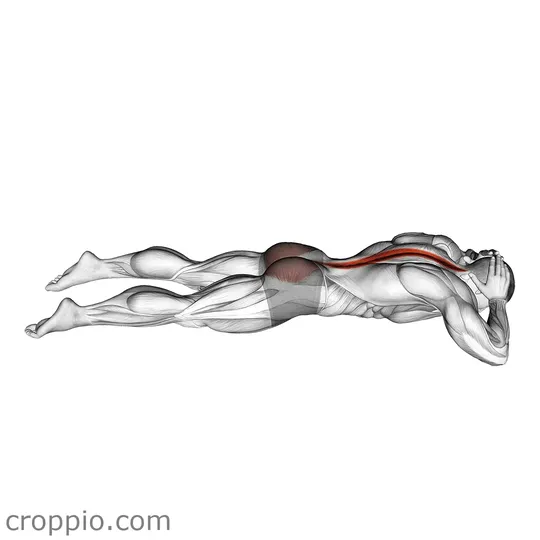
The floor back extensions exercise primarily targets the muscles of the lower back, specifically the erector spinae, which runs along the spine and is crucial for spinal extension and maintaining good posture. Additionally, this exercise engages the glutes and hamstrings as secondary muscles, providing support during the movement and contributing to overall lower body strength. The core also plays an important role in stabilizing the body throughout the exercise, making it a comprehensive movement for the posterior chain.
Top Mistakes
- Rounding the back: This can lead to strain on the spine. Ensure the back is straight throughout the movement.
- Overextending the back: Pushing too far up can cause discomfort and potential injury. Focus on controlled movements.
- Neglecting the core: Engaging the core is essential for stability; failing to do so can lead to poor form.
- Mechanical advantage: Lifting the legs too high can shift the focus away from the lower back, reducing effectiveness.
Execution Tips
To perform floor back extensions correctly, begin by lying face down on the floor with your legs extended and feet hip-width apart. Place your hands behind your head or crossed over your chest. Engage your core, keeping your back straight. As you lift your upper body off the ground, exhale and aim to bring your chest to a height where your body forms a straight line from your head to your toes. Hold for a moment at the top and then slowly lower back down to the starting position. Focus on using the muscles of your back and glutes rather than your arms or legs to lift.
Workouts
This exercise can be seamlessly incorporated into a variety of workout routines. Beginners may start with 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, focusing on form before progressing to more sets or reps. For added difficulty, consider supersets with complementary exercises such as planks or glute bridges to further enhance core stability and back strength. Advanced athletes can aim for 3-4 sets with 15-20 repetitions, integrating variations like holding the top position or incorporating resistance bands for increased challenge.
Conclusion
Floor back extensions offer significant benefits, including improved lower back strength, enhanced posture, and increased flexibility in the spine. By reinforcing the muscles that support the spine, this exercise plays a vital role in preventing back injuries and promoting a balanced physique. Regular incorporation of this exercise into your fitness routine can lead to noticeable improvements in overall strength and functional movement.