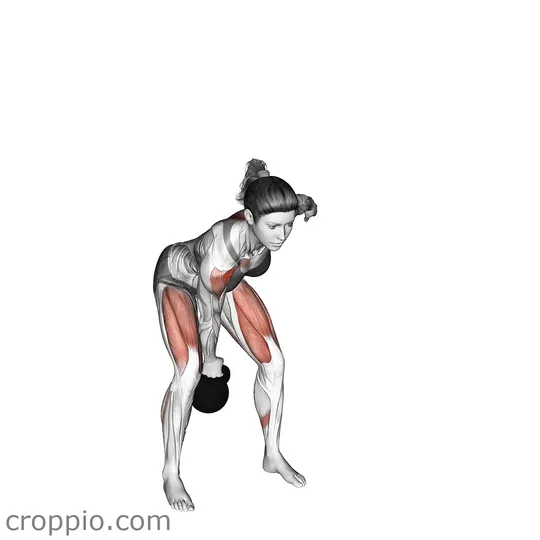
How To Do A Kettlebell Single Arm Swing
Latest Videos
No videos available.
How To Do A Kettlebell Single Arm Swing Workouts
Similar exercises
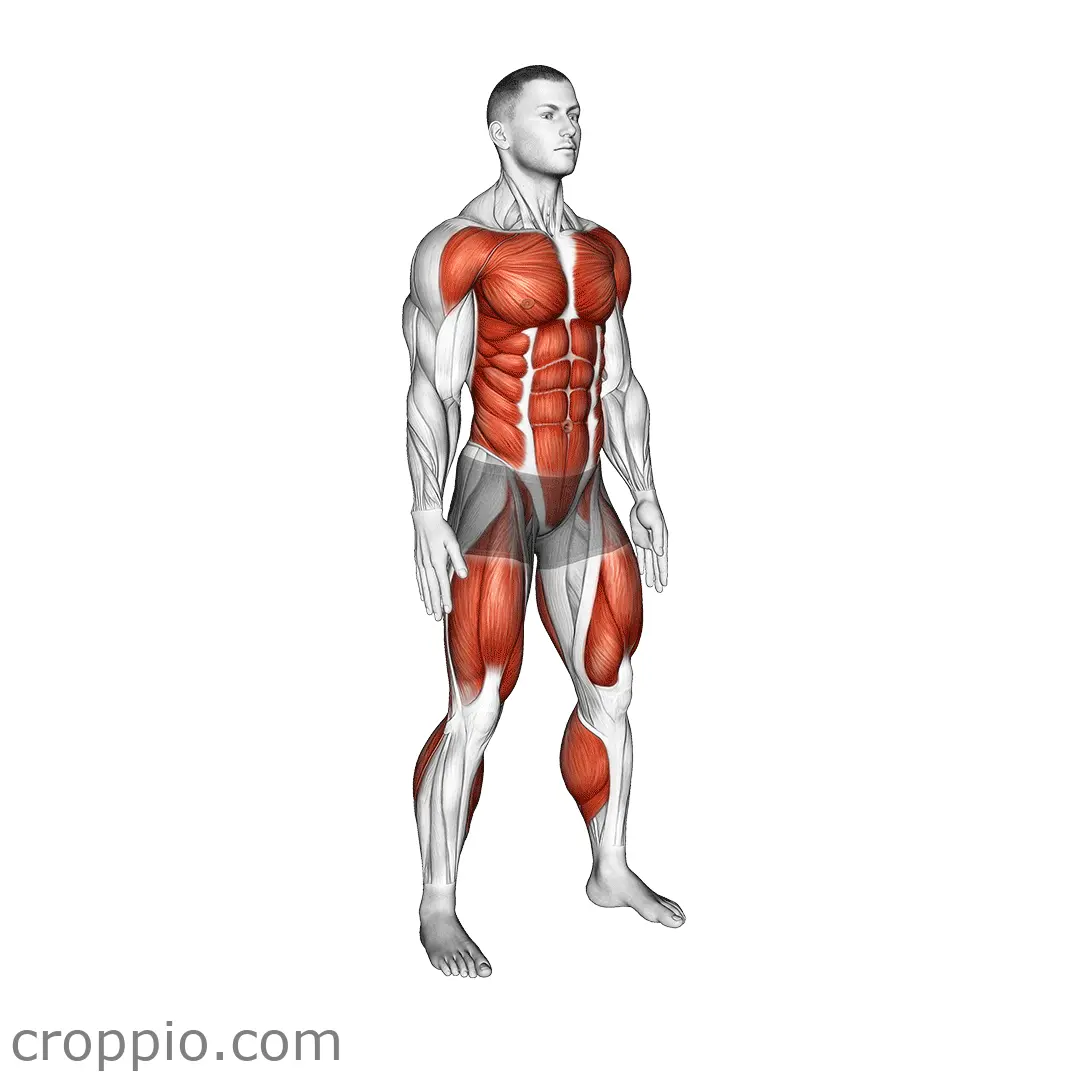
Muscles Involved
The kettlebell single arm swing is a dynamic exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, making it a powerful addition to any strength training routine. The primary muscles targeted include the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back, which are vital for hip extension and maintaining posture throughout the movement. Additionally, the shoulders, specifically the deltoids, engage to stabilize the kettlebell as it ascends and descends. Secondary muscles involved include the core muscles, particularly the transverse abdominis and obliques, which work to stabilize the torso against the rotational force generated by the swing. Overall, this full-body movement promotes functional strength and explosive power.
Top Mistakes
- Folding at the waist rather than bending at the hips can lead to back strain.
- Overextending the swing height may compromise form and lead to potential injury.
- Not engaging the core can cause instability, leading to improper mechanics.
- Using excessive arm strength instead of relying on the hips can diminish the effectiveness of the swing.
Execution Tips
- Begin with a neutral stance, feet shoulder-width apart, and the kettlebell positioned slightly in front of you.
- Hinge at the hips while keeping your back straight and lowering your body to grasp the kettlebell with one hand.
- Engage your core and drive your hips forward as you swing the kettlebell between your legs, keeping it close to your body for momentum.
- In one fluid motion, extend your hips and stand tall, swinging the kettlebell to shoulder height, with your wrist neutral.
- Let the kettlebell flow back down between your legs as you hinge at the hips again, maintaining control and stability.
Workouts
The kettlebell single arm swing can be effectively incorporated into a fitness routine in various ways. A typical session might include:
- 3 to 4 sets of 10 to 15 reps per side, ensuring adequate rest (30-60 seconds) between sets to maintain proper form.
- Pairing it with complementary exercises such as kettlebell deadlifts, push-ups, or squat variations for a well-rounded workout.
- Implementing it into a circuit training format, alternating between the single arm swing and other high-intensity movements.
Conclusion
The kettlebell single arm swing is not just an exercise; it’s a functional movement that builds coordination, balance, and overall athleticism. By effectively engaging multiple muscle groups, this dynamic movement enhances strength and endurance while promoting cardiovascular fitness. The versatility of this exercise makes it suitable for various fitness levels, ensuring that everyone can reap its benefits through proper form, consistency, and integration into a robust workout routine.