Cycling Muscles

Latest Videos
No videos available.
Cycling Muscles Workouts
Similar exercises
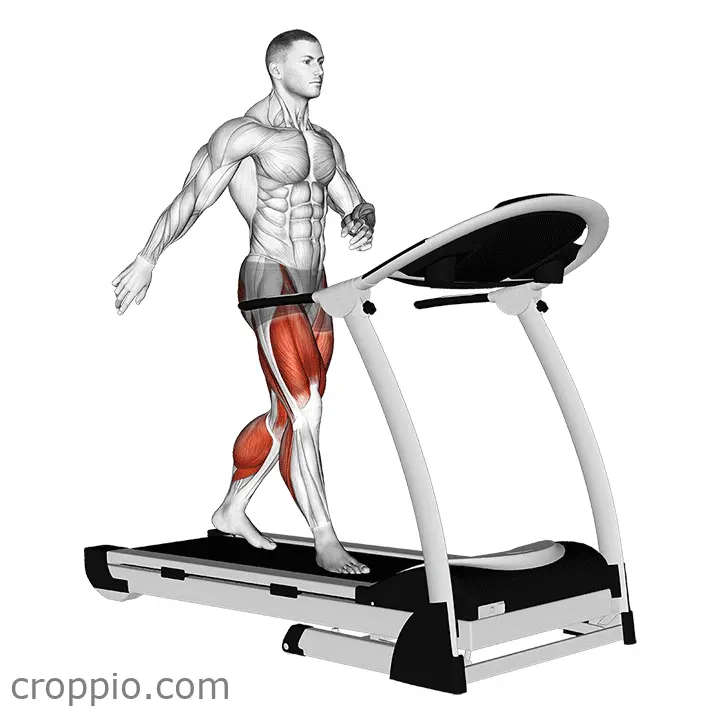
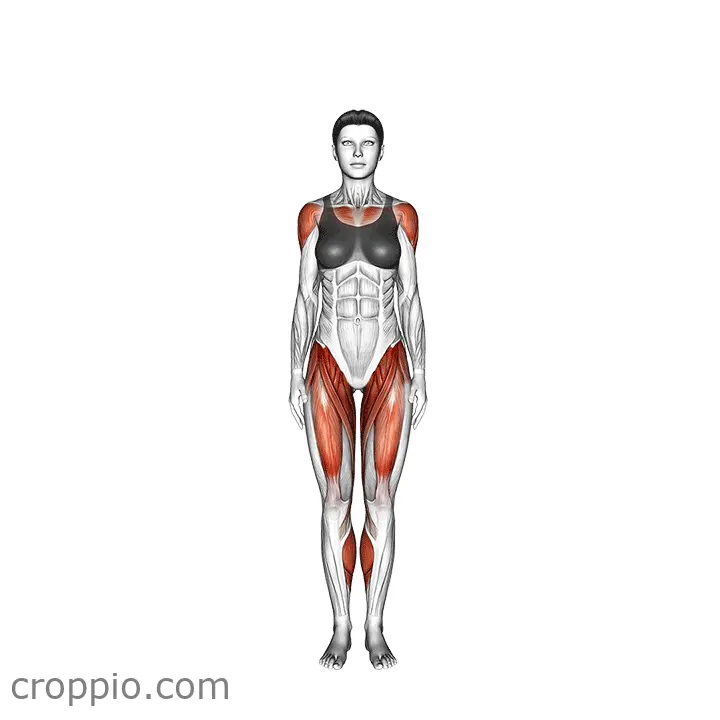
Muscles Involved
Cycling primarily targets the lower body, engaging several key muscle groups. The primary muscles involved are the quadriceps, which are the muscles located in the front of the thighs and are essential for extending the knee during pedaling. The hamstrings, located at the back of the thighs, also play a role by helping to flex the knee and stabilize the motion. The calves, especially the gastrocnemius and soleus, are activated during the push-off phase of the pedal stroke. Secondary muscles include the glutes, which contribute to the power generated during each pedal stroke, and the hip flexors, aiding in raising the knees during cycling. Additionally, cycling engages the core muscles to maintain stability and balance.
Top Mistakes
- Rounding the back: A hunched posture while cycling can lead to discomfort and potential injury.
- Incorrect saddle height: Sitting on a saddle that’s either too high or too low can affect leg extension and cause strain.
- Poor pedal technique: Using only the downward force and neglecting the upward pull can limit efficiency and muscle engagement.
Execution Tips
- Maintain a neutral spine: Try to keep your back straight and shoulders relaxed while cycling to avoid tension.
- Adjust your saddle height: Ensure your saddle is at a height where your leg is nearly fully extended at the bottom of the stroke, allowing for optimal power without strain.
- Use a full pedal stroke: Focus on pushing down and pulling up on the pedals to maximize muscle engagement and promote even development.
Workouts
Integrating cycling into your workout routine can enhance cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength. Aim for at least 3 cycling sessions per week. You could structure your workouts as follows:
- Steady state: 30-60 minutes of moderate-intensity cycling for endurance.
- Interval training: 15-20 minutes of alternating high-intensity cycling (1 minute) with low-intensity recovery (2 minutes).
- Complementary exercises: Combine cycling with squats or lunges to further build strength in the lower body.
Conclusion
Cycling is an excellent exercise that provides numerous benefits including improved cardiovascular endurance, enhanced muscular strength, and a low-impact alternative for joint health. Engaging multiple muscle groups while maintaining proper posture and technique can lead to effective results, making cycling a versatile addition to any fitness routine.