Back Extension
Back Extension Workouts
Similar exercises
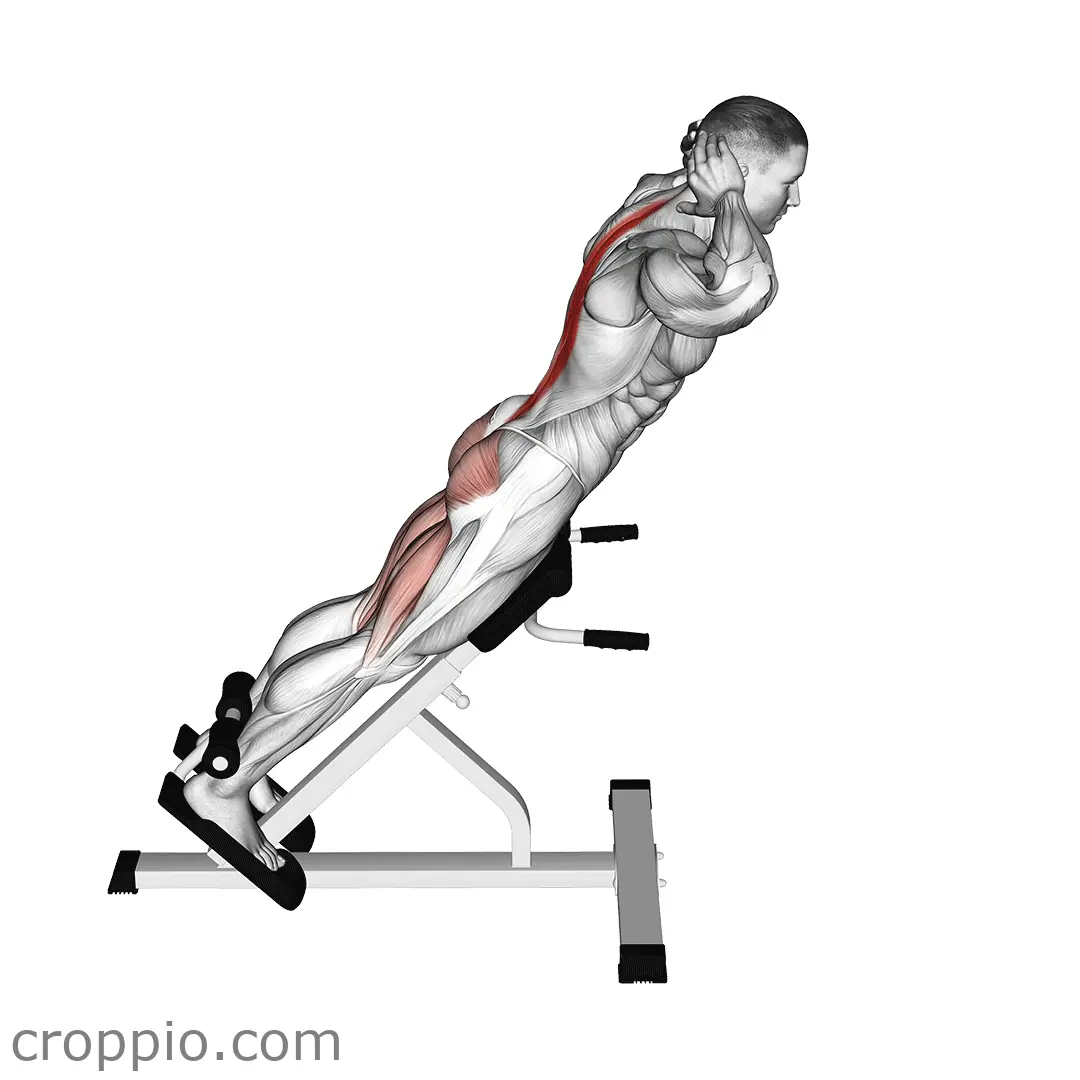
Muscles Involved
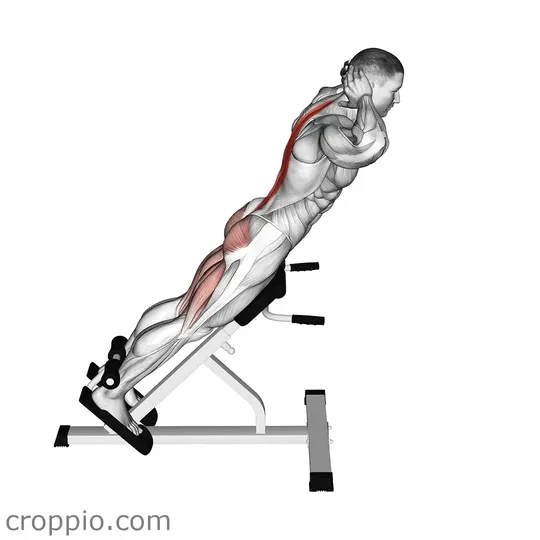
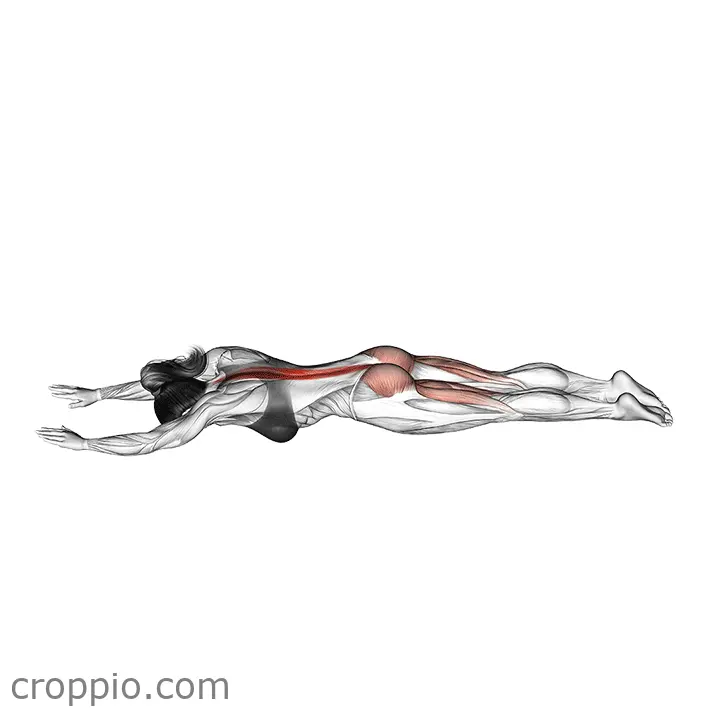
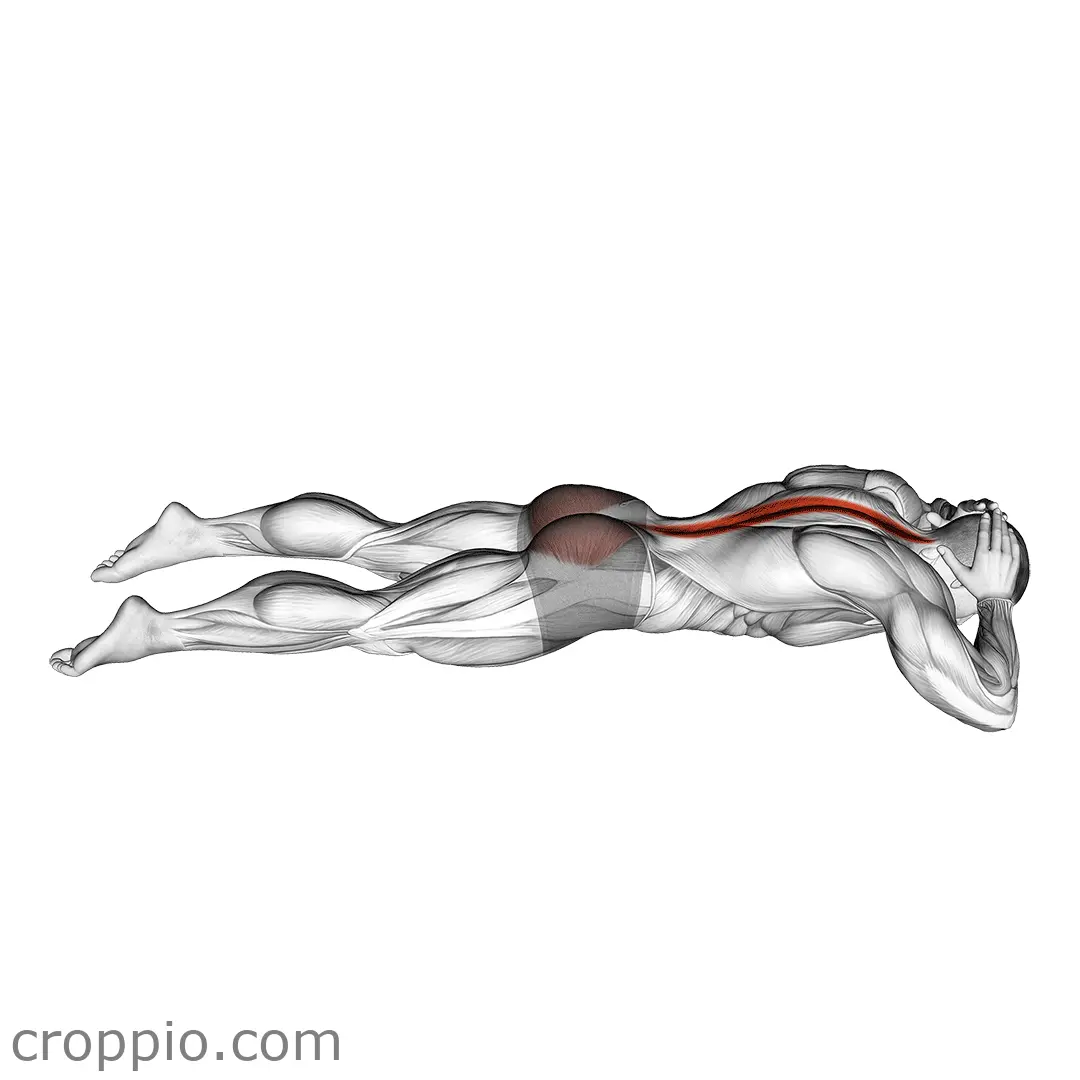
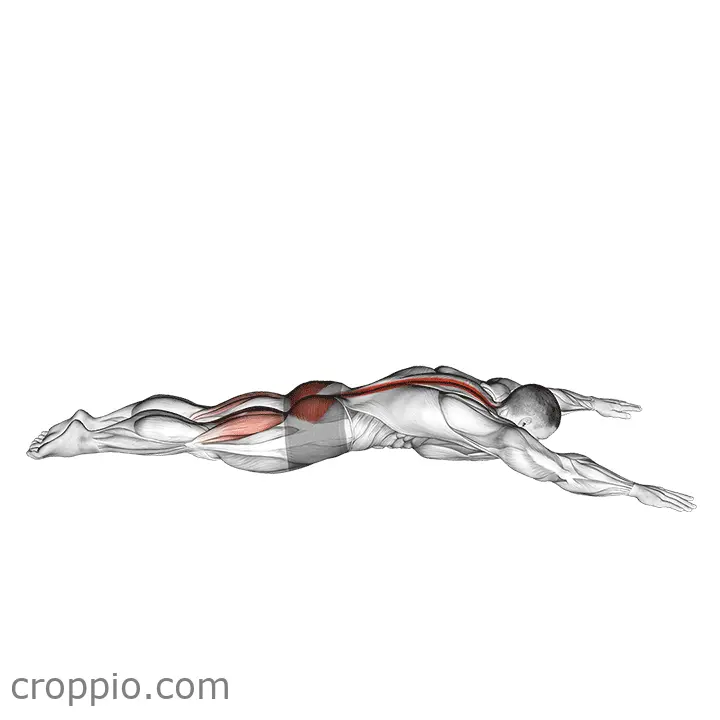
The back extension exercise primarily targets the erector spinae muscles, which run along the spine and are crucial for maintaining proper posture and spinal health. This exercise also engages several secondary muscles, including the glutes, hamstrings, and the multifidus, a small muscle located near the spine. By strengthening these muscle groups, back extensions help improve core stability and prevent lower back injuries.
Top Mistakes
- Overextending the back: Many individuals tend to arch their back excessively, which can lead to strain or injury.
- Raising the torso too high: Lifting beyond the neutral position can compress the spine and diminish the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Incorrect positioning: Failing to anchor the lower body properly can reduce focus on the back muscles and compromise form.
Execution Tips
- Start by lying face down on a back extension bench or stability ball, ensuring your hips are positioned at the edge and your feet are secured.
- Keep your neck in a neutral position, aligning it with your spine. Avoid looking up or tucking your chin excessively.
- Engage your core muscles before beginning the movement. This helps stabilize your spine and protects it from injury.
- Lift your torso to a horizontal position, squeezing your glutes and engaging your lower back. Keep the movement controlled and gradual.
- Lower back down slowly, avoiding jerky motions to maintain tension in the muscles throughout the exercise.
Workouts
Incorporate back extensions into your strength training routine by performing 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions. Ensure adequate rest between sets, around 30-60 seconds, to allow for recovery. This exercise can be effectively combined with complementary moves such as planks, deadlifts, or squats to enhance overall back and core strength. For a balanced workout, aim to integrate back extensions 2-3 times a week, ensuring your entire back muscle group is systematically engaged.
Conclusion
Back extensions are a powerful exercise for strengthening the lower back and associated muscle groups. By improving muscular endurance and stability, this exercise significantly contributes to better posture, reduces the risk of back injuries, and enhances athletic performance. Regular incorporation of back extensions into your routine not only promotes a strong foundation for various physical activities but also aids in day-to-day functional movements.