Wood Chop Muscles
Wood Chop Muscles Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
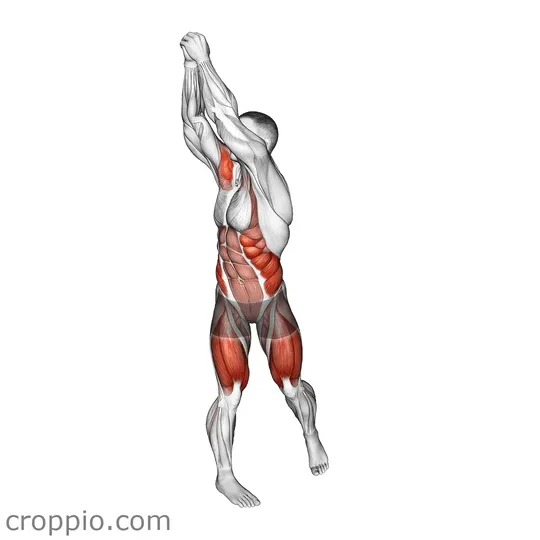
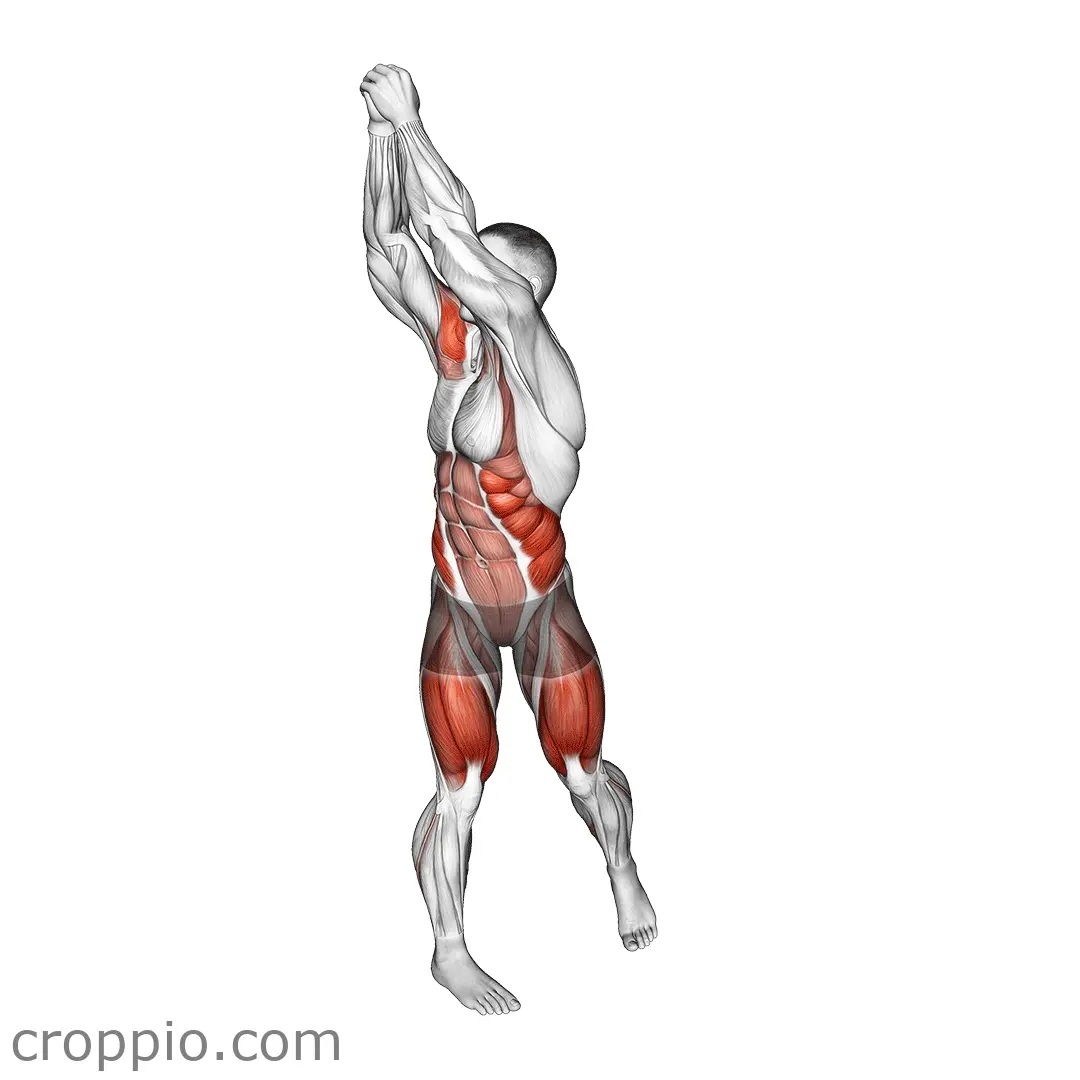
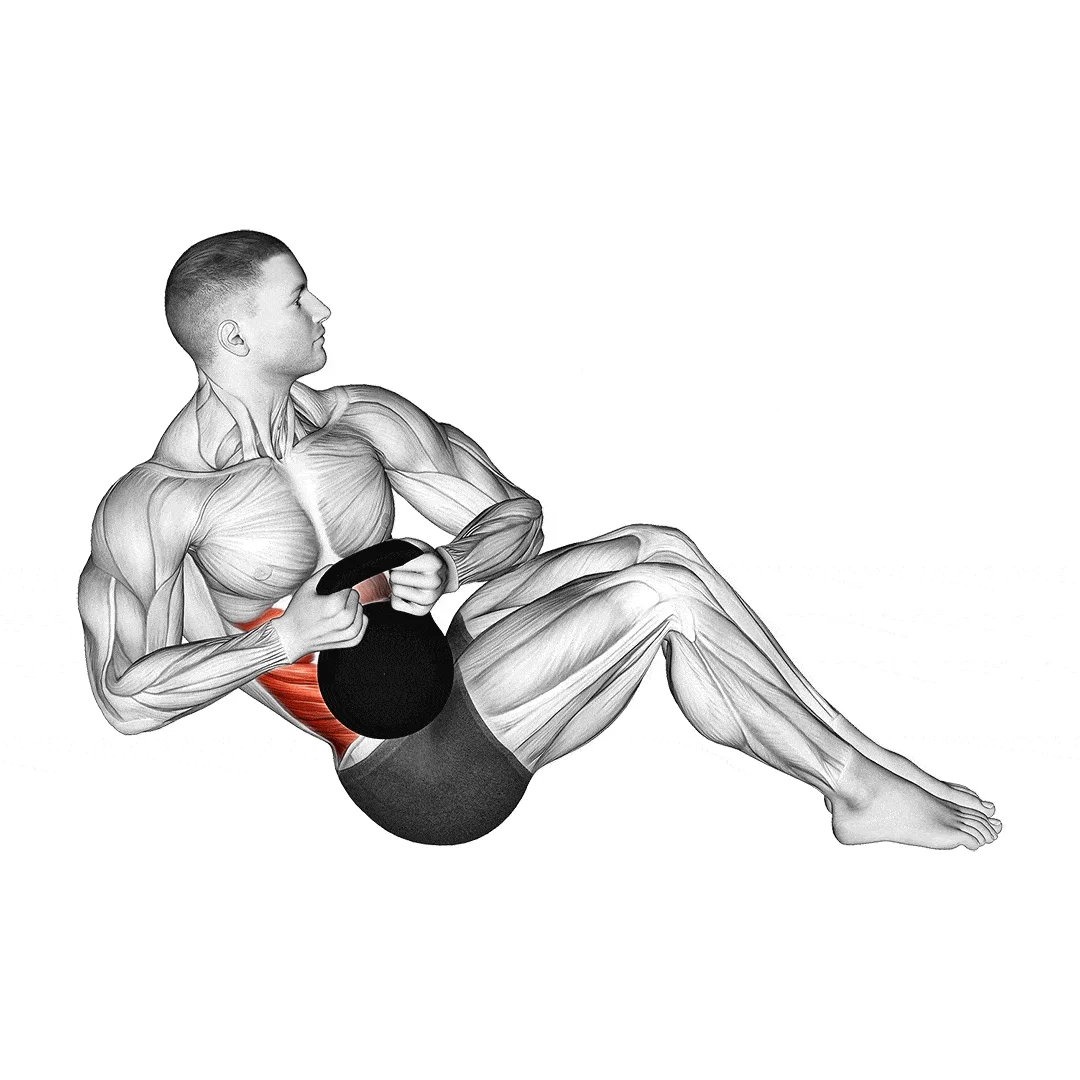
The wood chop exercise primarily targets the oblique muscles, responsible for rotation and lateral flexion of the torso. In addition to the obliques, this exercise engages the rectus abdominis, providing core stability and strength. Secondary muscles activated include the latissimus dorsi, which aids in arm movement, and the gluteal muscles, which support hip stability during the chopping motion. The combination of these muscle groups contributes to improved functional strength, especially beneficial for athletes and those involved in sports requiring rotational power.
Top Mistakes
- Improper stance: Standing too narrow or too wide can lead to imbalance.
- Ignoring hip movement: Failing to engage the hips reduces power and risks injury.
- Incorrect weight transfer: Not shifting weight between legs during movement can strain the lower back.
- Overextending arms: Using just arm strength instead of incorporating the core and legs leads to ineffective execution.
Execution Tips
- Start with a balanced stance: Keep feet shoulder-width apart for stability.
- Engage your core: Activate your abdominal muscles before initiating the movement to protect your lower back.
- Use a fluid motion: Begin the chop above your shoulder and follow through to the opposite hip in a controlled manner.
- Maintain a neutral spine: Avoid rounding or arching your back; keep it straight throughout the exercise.
Workouts
To effectively incorporate wood chops into your workout routine, aim to perform 3 to 4 sets of 10 to 15 repetitions on each side. This exercise can be complemented by related movements such as Russian twists, medicine ball slams, and planks, which target the core from different angles. Including wood chops in a circuit that emphasizes full-body workouts will help enhance muscular endurance and core stability.
Conclusion
The wood chop exercise stands out as an efficient way to build core strength while enhancing rotational power, thereby benefiting athletic performance and daily function. By focusing on proper form, avoiding common mistakes, and integrating it into a diverse routine, you can maximize the advantages of this dynamic movement. Regular practice of wood chops not only strengthens key muscle groups but also promotes better posture and functional movement patterns.