Supermans
Supermans Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
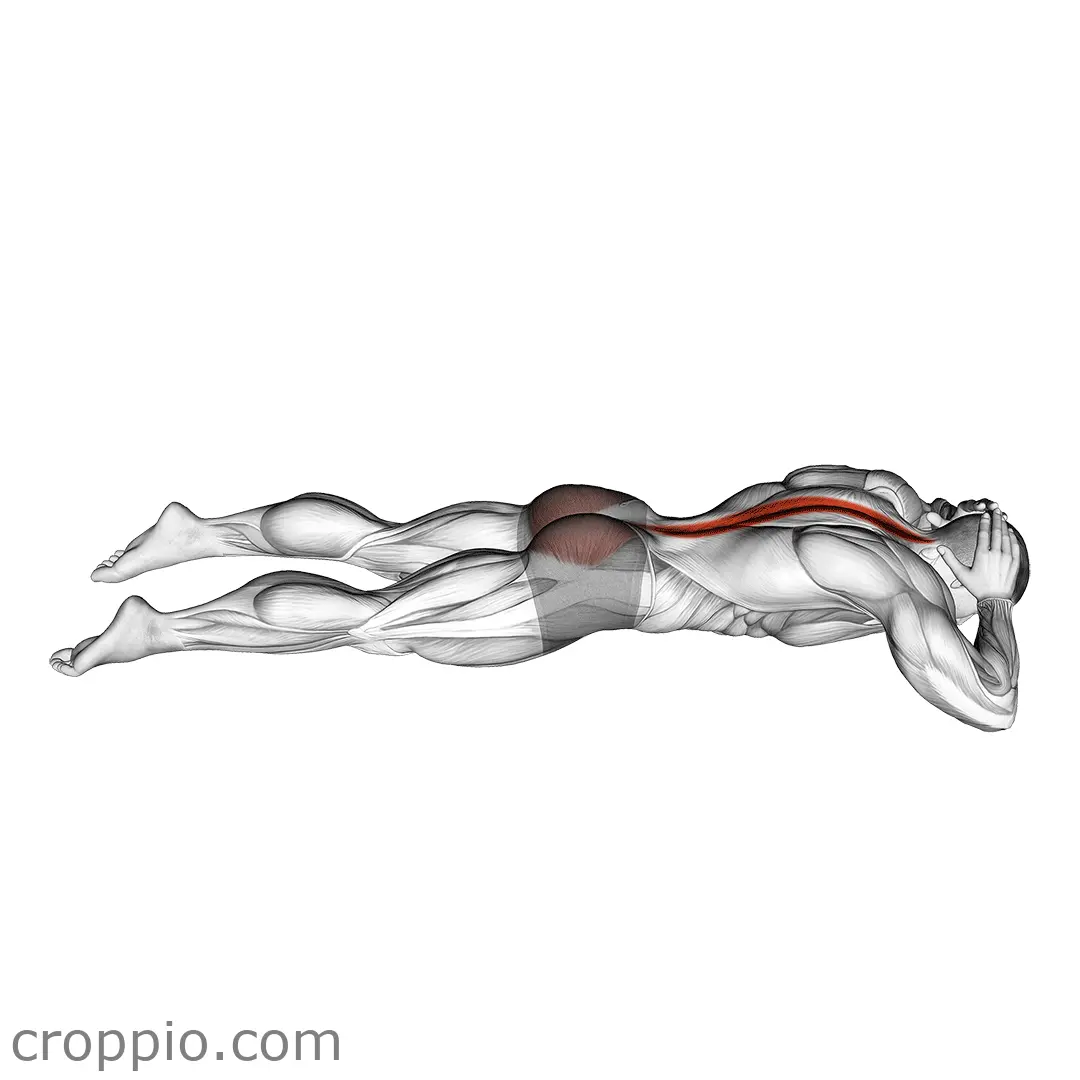
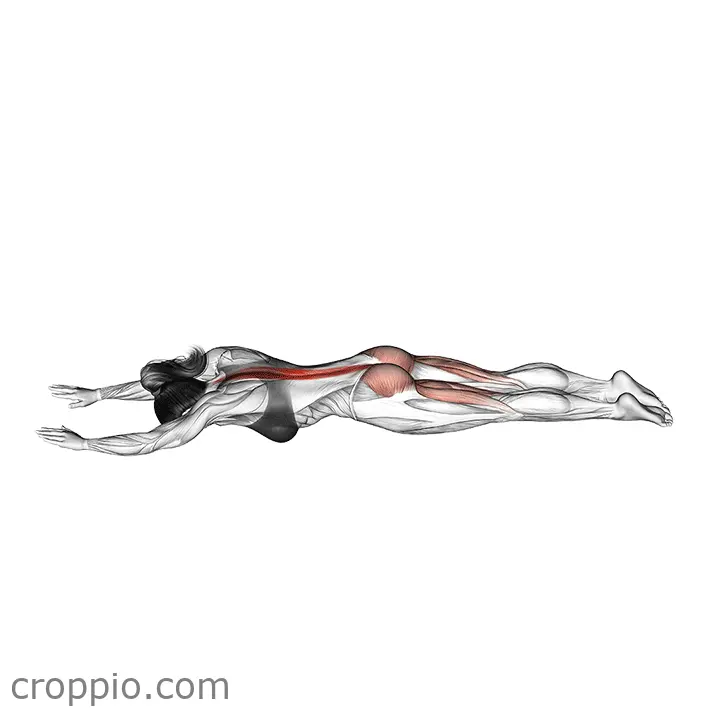
The Superman exercise primarily targets the muscles of the lower back, specifically the erector spinae, which runs along the spine. This exercise also engages the glutes, hamstrings, and the muscles of the shoulders and upper back. By lifting both the arms and legs off the ground simultaneously, it promotes strength in the posterior chain, improving stability and posture.
Top Mistakes
- Raising the arms or legs too high: This can lead to hyperextension of the lower back, causing strain.
- Holding the breath: Many people forget to breathe during the exercise, which is crucial for maintaining tension in the core and preventing unnecessary fatigue.
- Arching the neck: Straining the neck upwards can lead to discomfort; instead, aim to keep a neutral neck position.
Execution Tips
- Begin by lying face down on a comfortable surface, with arms extended in front of you and legs straight behind.
- As you inhale, simultaneously lift your arms, chest, and legs off the ground, aiming to engage your back and glutes without overarching your back.
- Keep your gaze downwards to maintain a neutral spine and avoid straining your neck.
- Hold the raised position for a count of two to five seconds, then gently lower back down as you exhale.
Workouts
The Superman exercise can be an excellent addition to various workout routines, particularly those aimed at enhancing core strength and stability. For optimal results, consider incorporating it into your routine with the following guidelines:
- Perform 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, allowing for 30 seconds of rest between sets.
- Pair it with exercises like planks and bird-dogs, which target similar muscle groups for a comprehensive back and core workout.
- Include it in a full-body routine, ensuring to balance it with exercises targeting the anterior muscles, such as push-ups or lunges.
Conclusion
The Superman exercise is a simple yet effective movement that enhances strength and stability in the back, glutes, and shoulders. By avoiding common mistakes and focusing on execution, you can build a strong posterior chain that contributes to better posture, improved athletic performance, and reduced risk of injury. Incorporating this exercise into your routine will not only make you stronger but also contribute to overall spinal health.