Reverse Deficit Lunge

Latest Videos
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
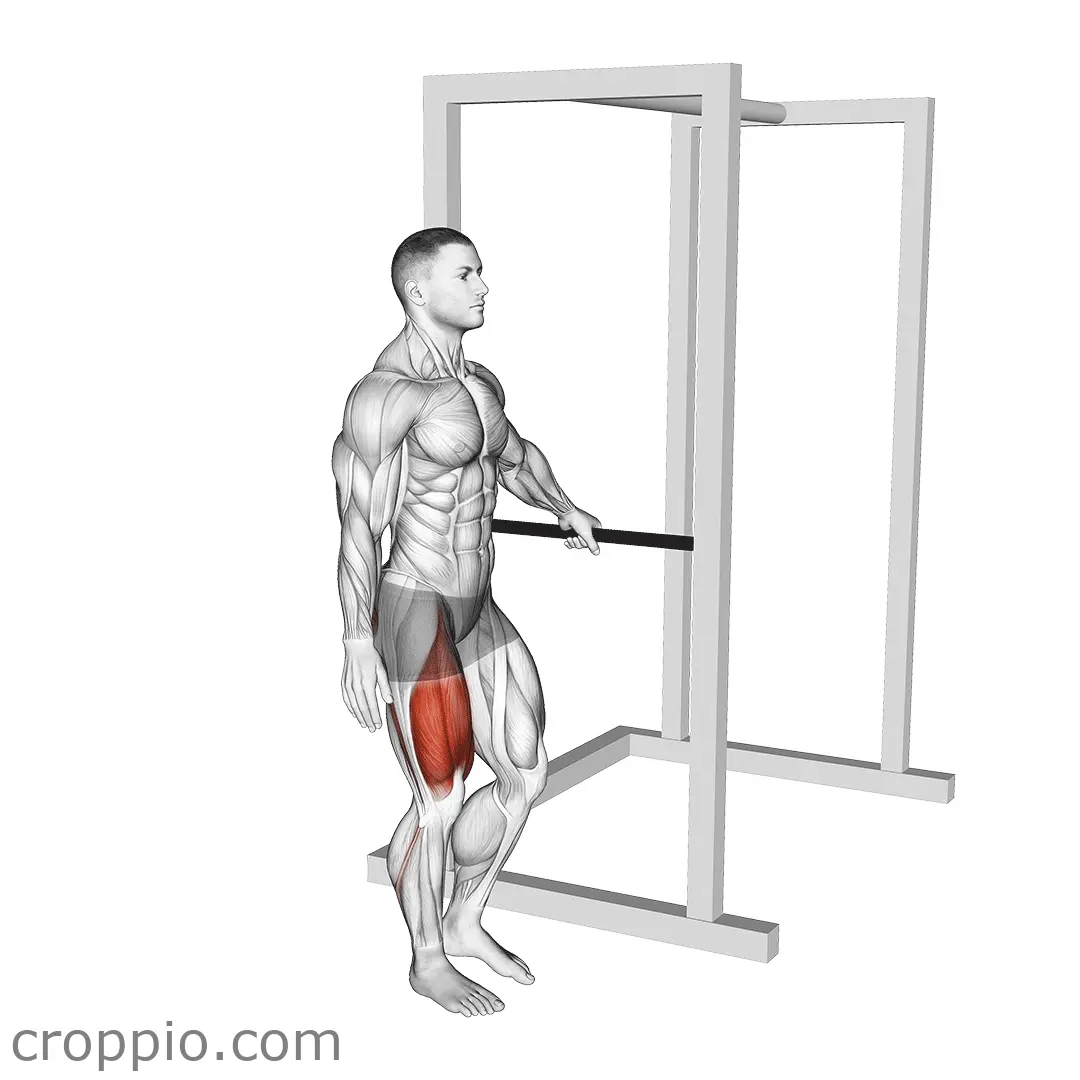
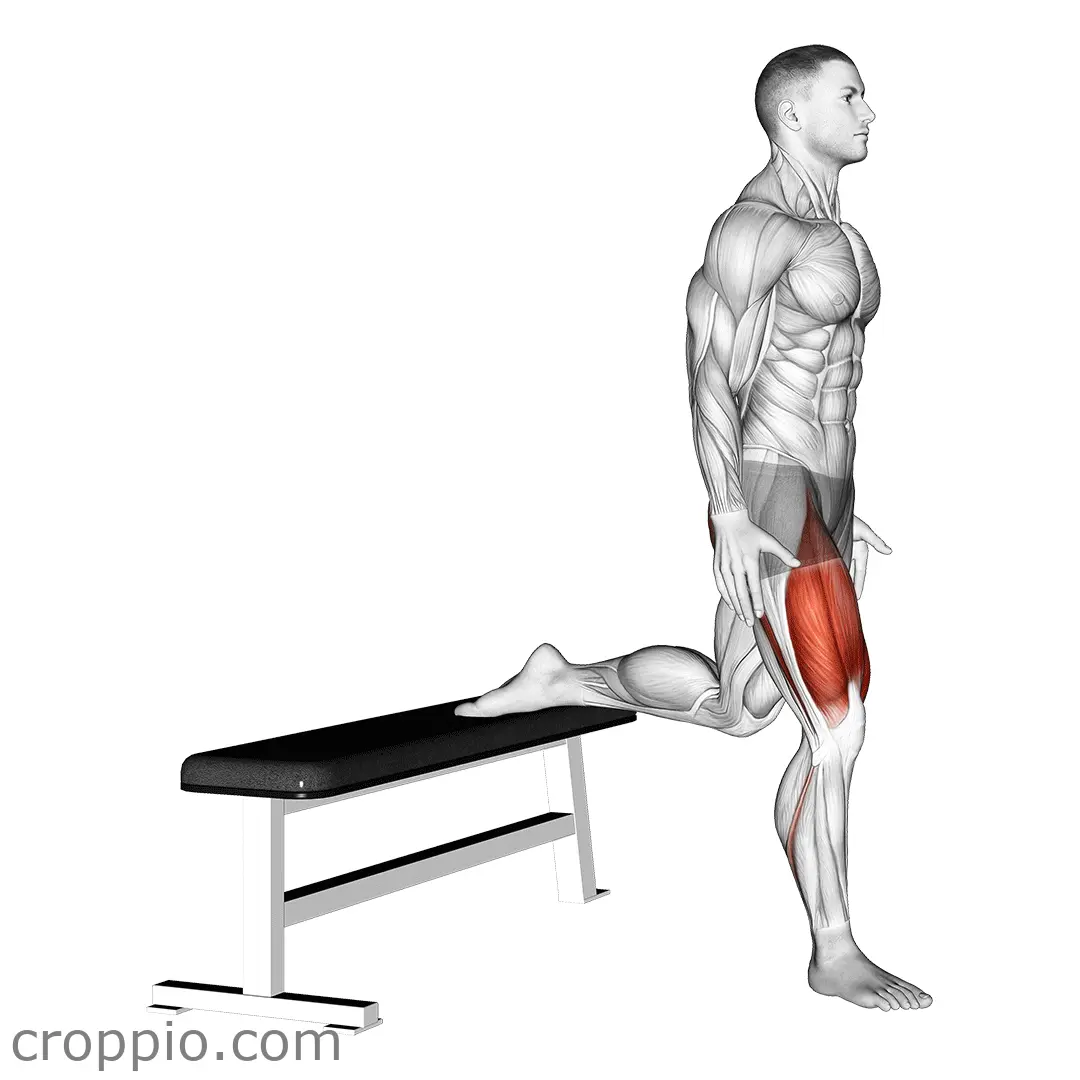
The reverse deficit lunge is a highly effective lower body exercise that primarily targets the gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and quadriceps. This exercise involves stepping backward and lowering the hips, which emphasizes the glutes and hamstrings more than a standard lunge. Additionally, the movement engages the core musculature, including the rectus abdominis and obliques, as they stabilize the torso throughout the exercise. Secondary muscles involved include the calves and hip flexors, facilitating the movement and contributing to overall leg strength.
Top Mistakes
- Insufficient range of motion: Not lowering the back knee close enough to the ground can diminish the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Improper knee alignment: Allowing the front knee to cave inwards instead of staying aligned over the ankle can lead to injury.
- Leaning forward: Maintaining an upright torso is crucial; leaning too far forward takes the focus away from the targeted muscles.
- Lack of depth: Failing to engage your hips adequately by standing too upright can lessen the benefits of the exercise.
Execution Tips
- Start with good posture: Stand tall with your feet shoulder-width apart and engage your core before beginning the movement.
- Step back carefully: Take a controlled step backward with one leg, ensuring your back knee approaches the ground without touching it.
- Focus on your front leg: Keep your front knee directly above your ankle to maintain joint integrity and support.
- Return to starting position: Use the strength of your front leg to push back up to the starting position while keeping your torso upright.
Workouts
The reverse deficit lunge can be integrated into a comprehensive lower body workout. Aim for 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions on each leg to build strength and endurance. This exercise pairs well with other lower body movements such as squats, deadlifts, or lateral lunges for a balanced routine. For added intensity, consider incorporating weights such as dumbbells or a barbell, or try adding plyometric variations for increased power.
Conclusion
In summary, the reverse deficit lunge is an excellent exercise for building lower body strength and enhancing core stability. By targeting key muscle groups, it not only strengthens the legs but also improves balance and coordination. Avoiding common mistakes and following proper technique will maximize the effectiveness of this exercise and contribute to overall athletic performance.