Plank Movement
Plank Movement Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
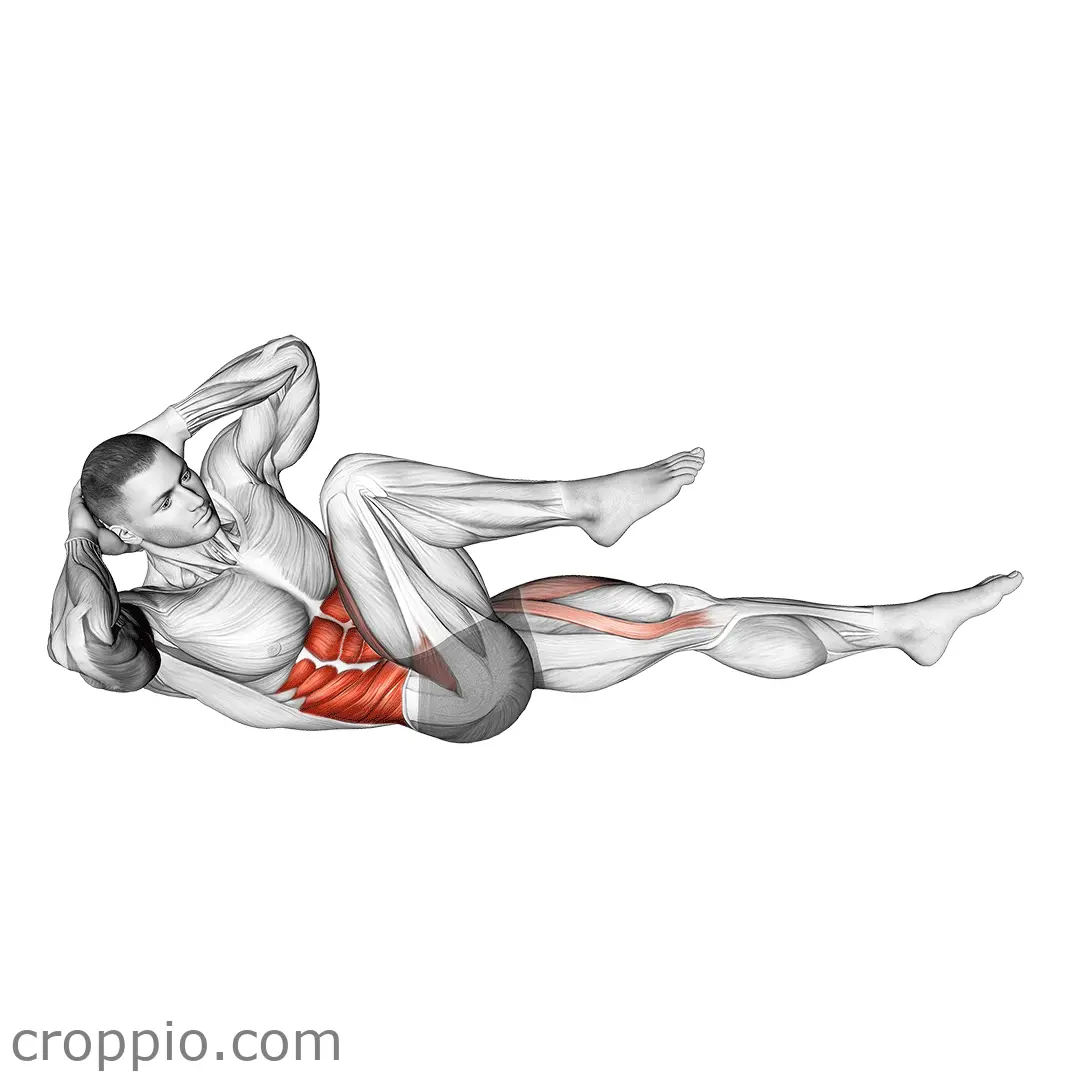
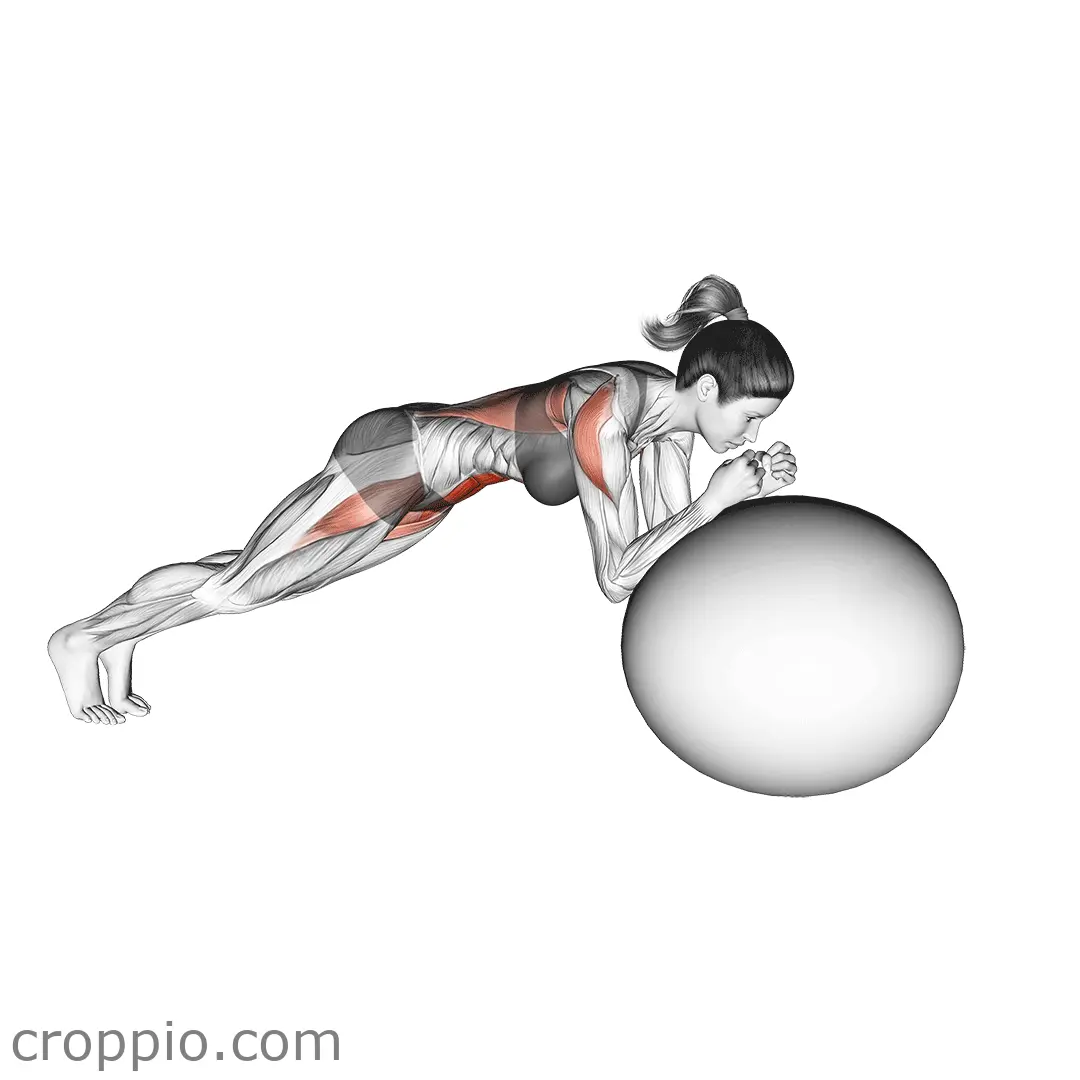
The plank movement primarily targets the core muscles, providing a robust workout for the rectus abdominis (the "six-pack" muscles) and the transverse abdominis, which is crucial for stabilizing the spine. Additionally, the internal and external obliques are engaged, improving rotational strength. Secondary muscles include the shoulders, particularly the deltoids, and the muscles in the lower back, such as the erector spinae. The plank also activates the glutes and the quadriceps, making it a comprehensive exercise that benefits multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
Top Mistakes
- Lack of alignment: Allowing the hips to sag or rise too high disrupts form and reduces effectiveness.
- Holding breath: Failing to breathe properly can lead to muscle tension and fatigue more quickly.
- Overextending neck: Looking forward instead of keeping the neck neutral can cause strain.
- Incorrect arm placement: Positioning the arms too far from the body can cause instability.
Execution Tips
- Start on all fours: Begin in a tabletop position, with your wrists aligned directly under your shoulders and knees under your hips.
- Extend legs: Tuck your toes under and extend your legs back, keeping the body straight from head to heels.
- Engage your core: Pull your belly button towards your spine to activate your core muscles effectively.
- Maintain neutral spine: Ensure your head, neck, and spine are aligned in a straight line, avoiding excessive curvature.
- Stay still: Keep your body stable and avoid rocking or swaying, which can diminish benefits.
Workouts
The plank can be effectively incorporated into various workout routines. Consider adding it to a core circuit, holding the plank for 30 seconds to 1 minute, depending on your fitness level. Aim for 3 to 5 sets with 30 seconds of rest in between. To enhance the challenge, pair the plank with complementary exercises like push-ups, mountain climbers, or side planks. This combination increases heart rate and engages additional muscles, ensuring a well-rounded workout.
Conclusion
The plank movement is a highly beneficial exercise that enhances core stability, improves posture, and boosts overall strength. By engaging multiple muscle groups, it not only targets the abs but also strengthens the shoulders, back, and glutes. Additionally, its versatility allows it to be easily integrated into any fitness regimen, catering to all levels. Regular practice of the plank can lead to improved athletic performance and reduced risk of injury, making it an essential addition to your exercise routine.