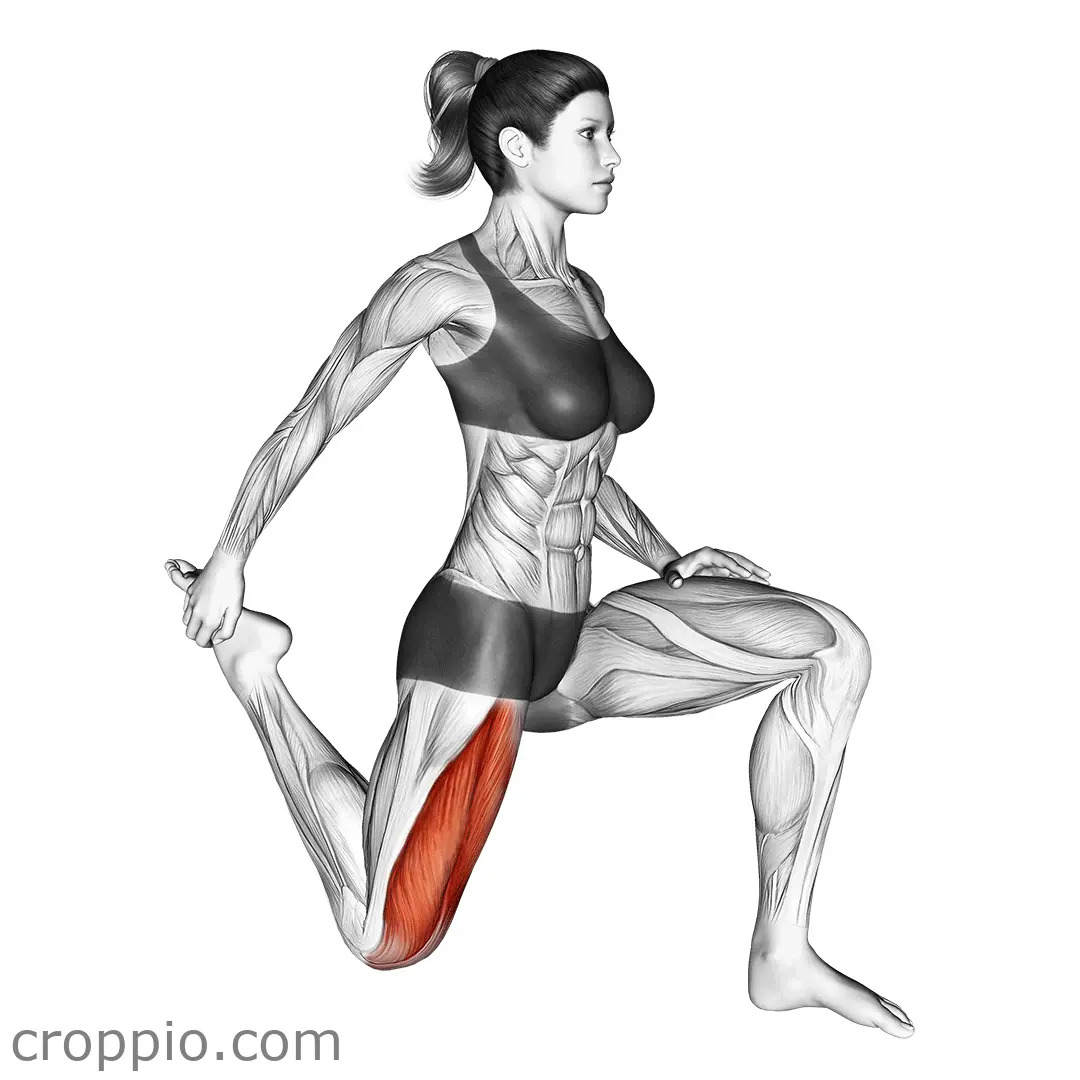
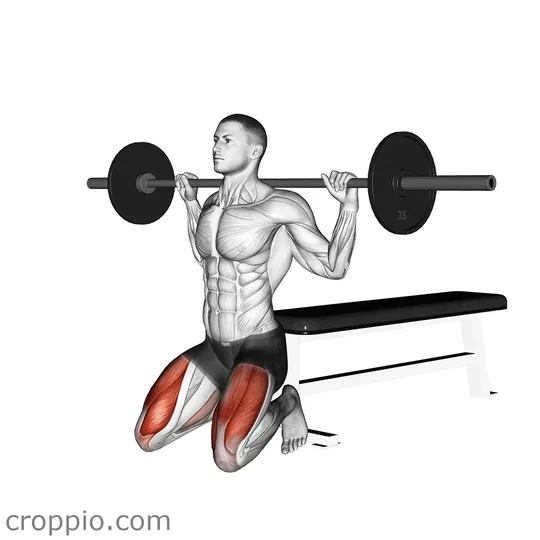
How To Do A Kneeling Squat

Latest Videos
No videos available.
Similar exercises
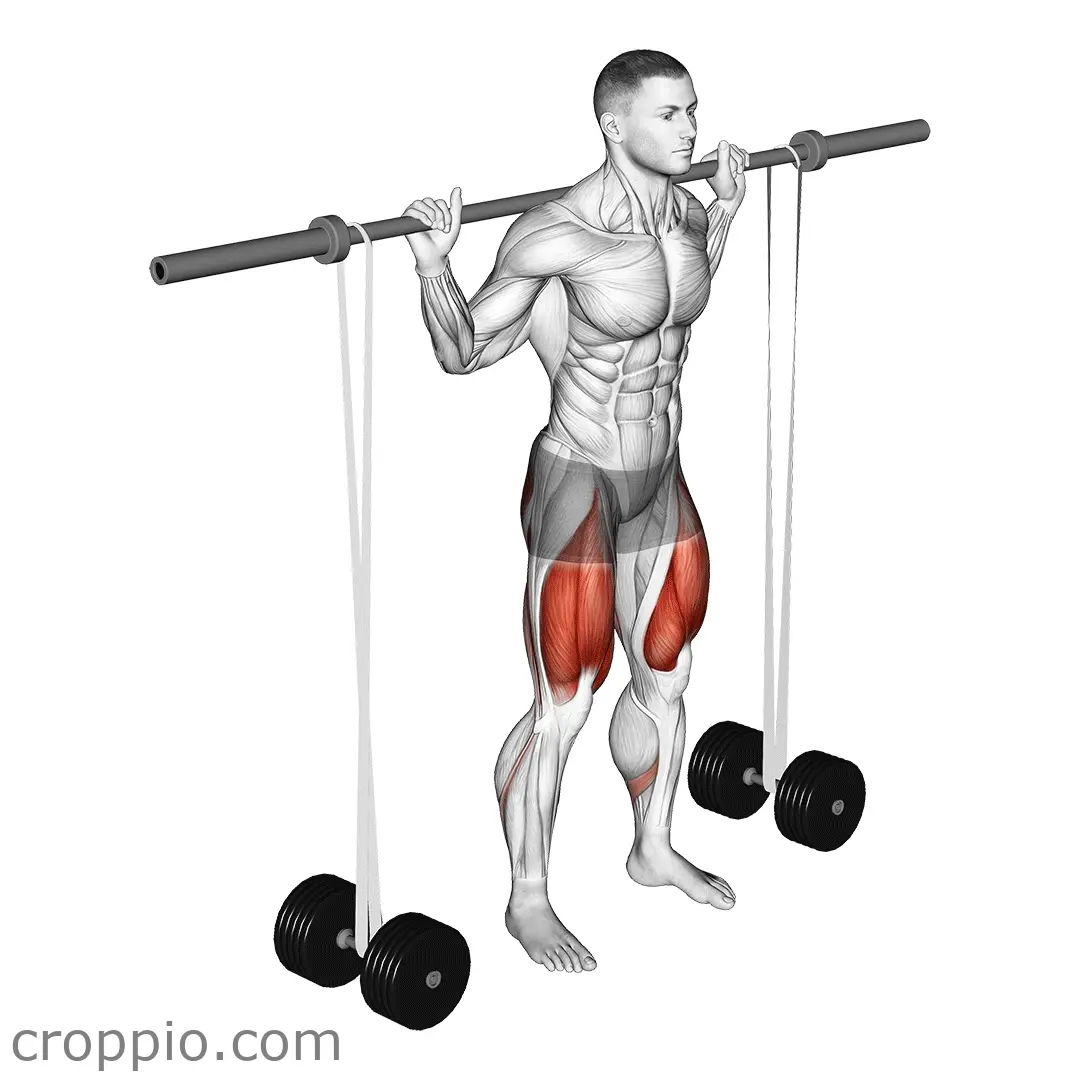
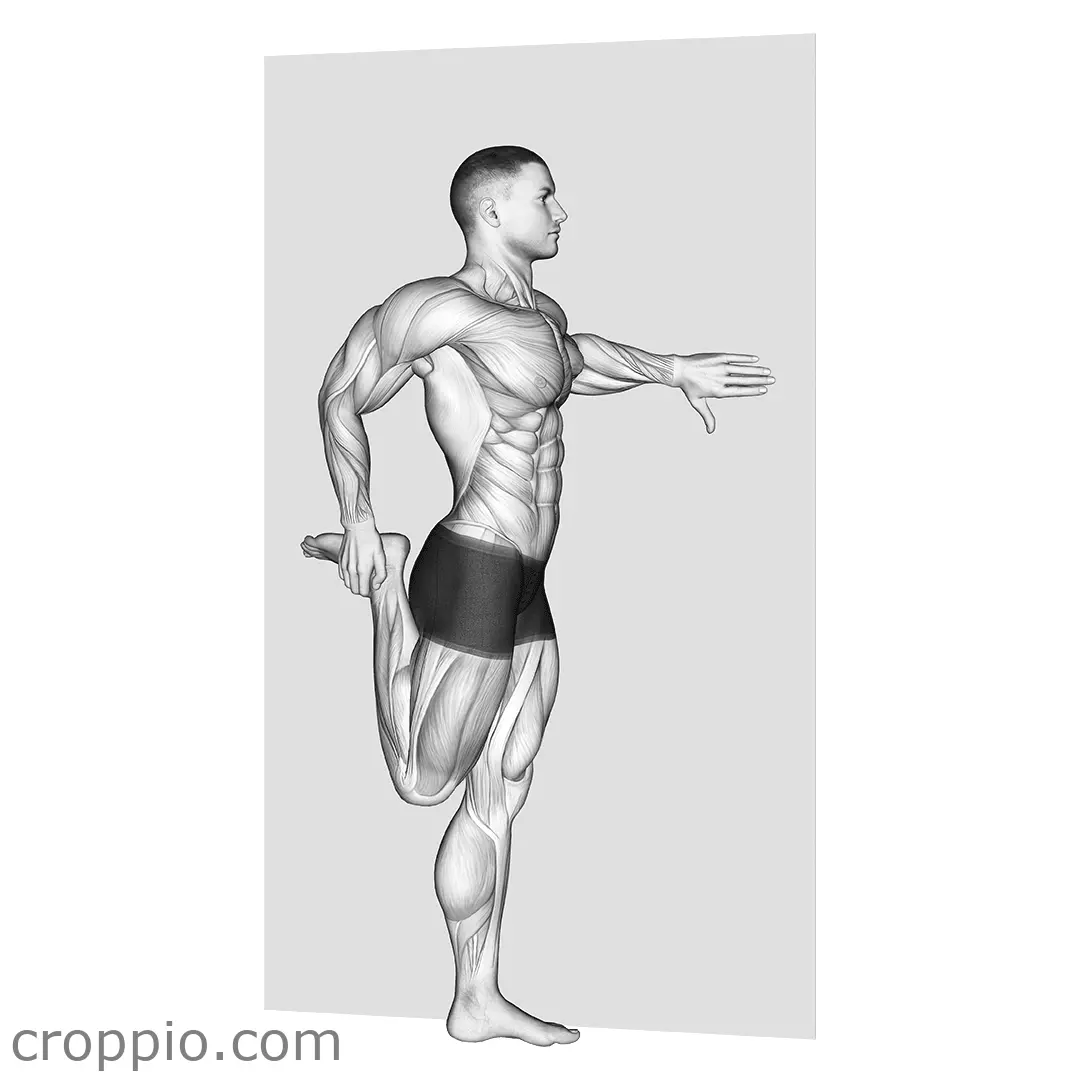
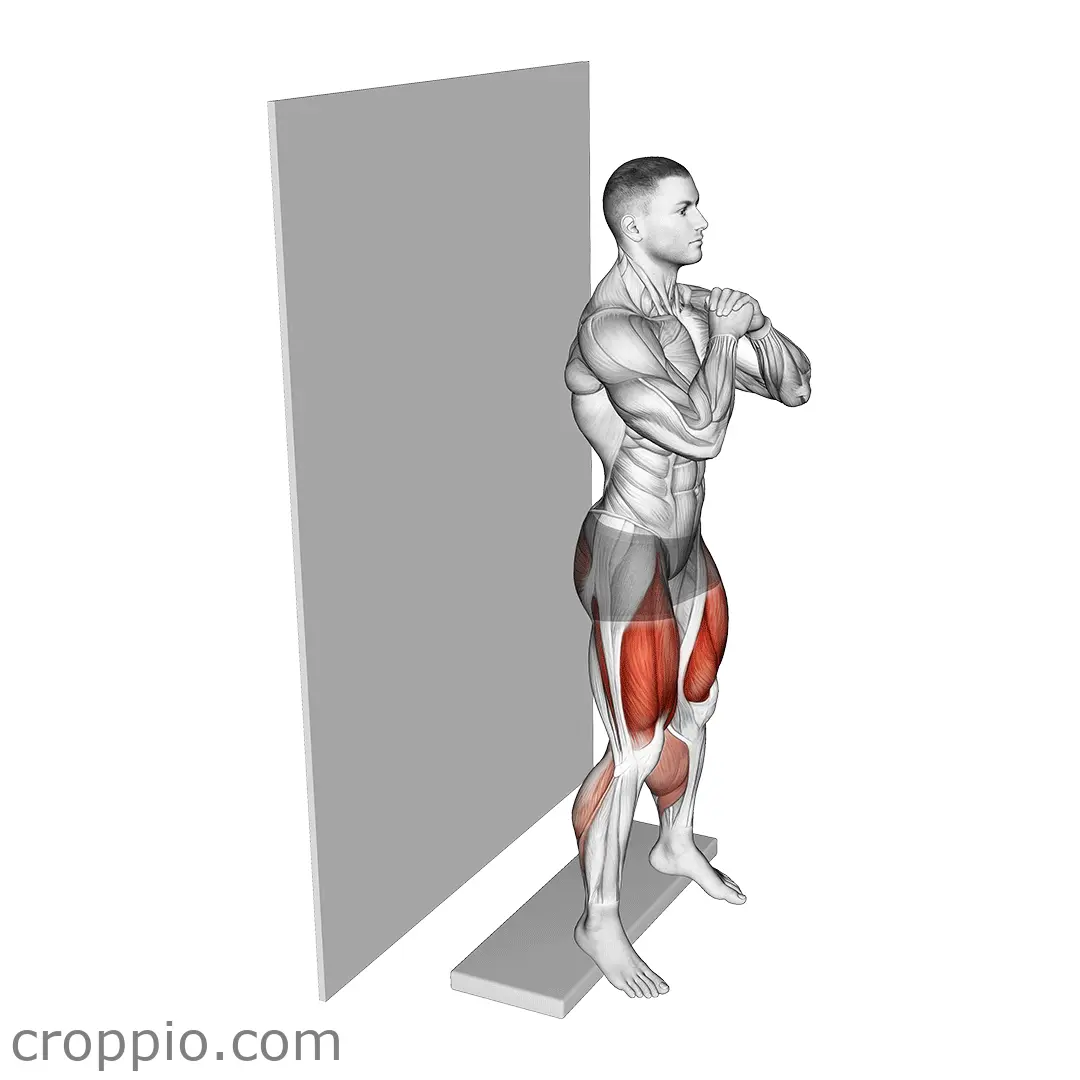
Muscles Involved
The kneeling squat primarily targets the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings, making it an excellent lower body strength builder. As you descend into the squat, your abdominal muscles and lower back engage to provide stability and support, classifying them as secondary muscles involved in this movement. Additionally, the hip flexors are activated, helping to maintain proper posture throughout the exercise. This combination of muscles not only enhances strength but also contributes to improved mobility and coordination.
Top Mistakes
- Allowing the knees to extend past the toes, which can strain the joints.
- Failing to keep the back straight, leading to potential strain and injury.
- Not engaging the core, which can destabilize the body and diminish effectiveness.
- Using momentum rather than controlled movement, reducing muscle engagement.
Execution Tips
To perform a kneeling squat correctly, start by kneeling on a padded surface with your knees hip-width apart. Position your feet flat on the ground behind you, toes pointed slightly outward. Engage your core while keeping your chest lifted and look forward. Slowly lower your hips back towards your heels as if sitting into a chair. Breathe normally and descend until your thighs are parallel to the ground, making sure to keep your knees in line with your toes. Hold the squat position for a brief moment before returning to the starting position by pushing through your heels.
To ensure the best results, perform this exercise in a controlled manner, focusing on form over speed. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to monitor your alignment.
Workouts
The kneeling squat can easily integrate into various workout routines. For beginners, start with 3 sets of 8-12 reps, focusing on mastering the technique before increasing the intensity. As you progress, you can add weights, such as dumbbells or a kettlebell, to increase resistance. The kneeling squat pairs well with complementary exercises like lunges or glute bridges for a well-rounded lower body workout. Additionally, incorporating mobility exercises can enhance joint flexibility and prevent injury.
Conclusion
The kneeling squat is a valuable exercise that builds strength, improves flexibility, and enhances overall lower body stability. By focusing on proper form and avoiding common mistakes, you can maximize the effectiveness of this exercise and reap its benefits in strength training. Incorporating it into your fitness routine can lead to better posture, improved athletic performance, and decreased risk of injury.