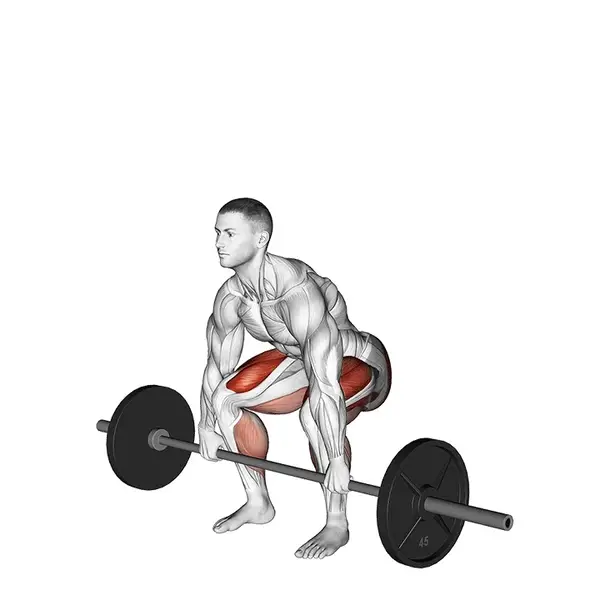
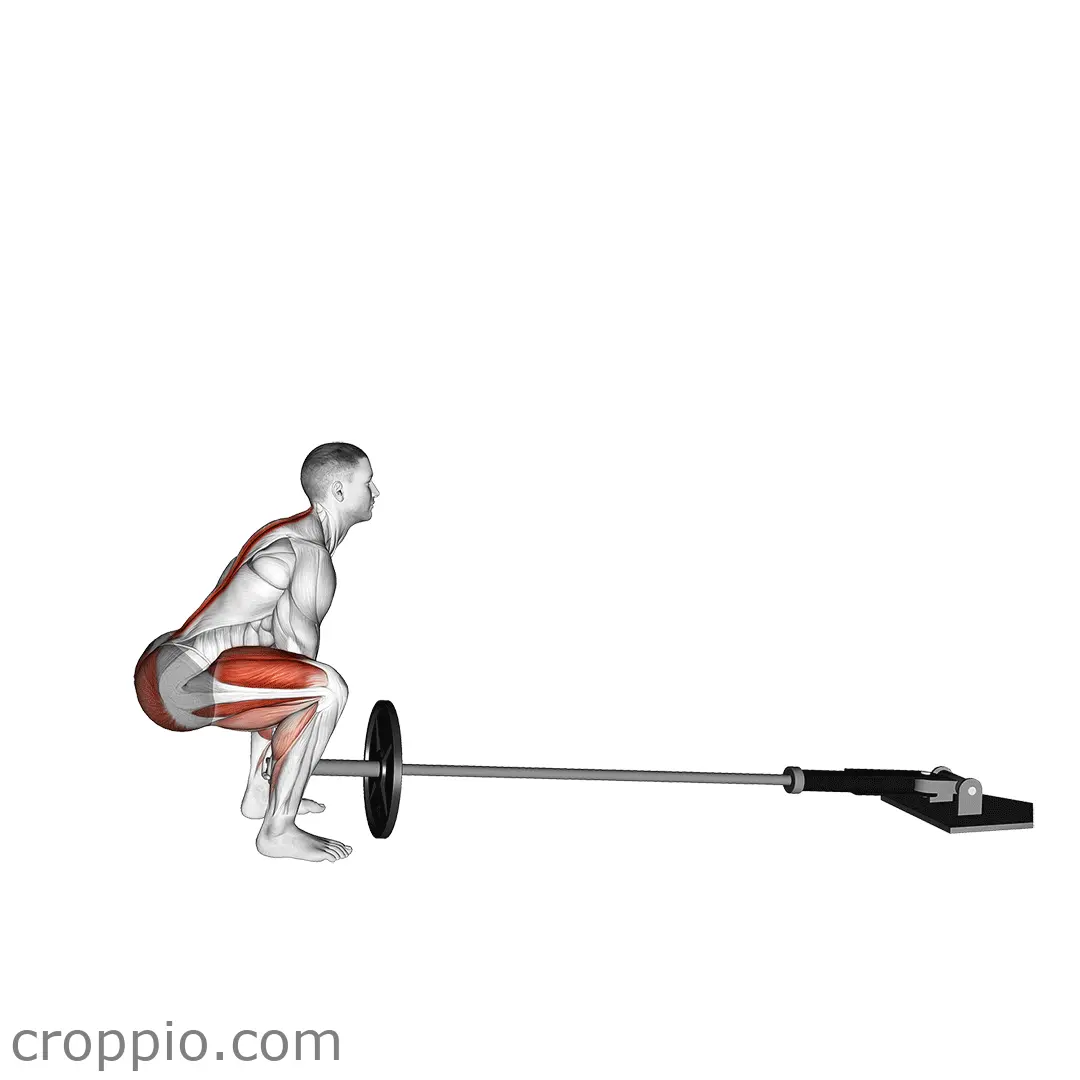
Hex Bar Deadlift
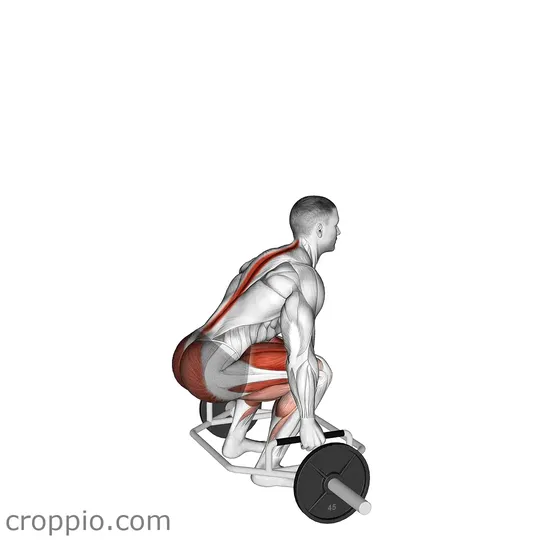
Latest Videos
No videos available.
Hex Bar Deadlift Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
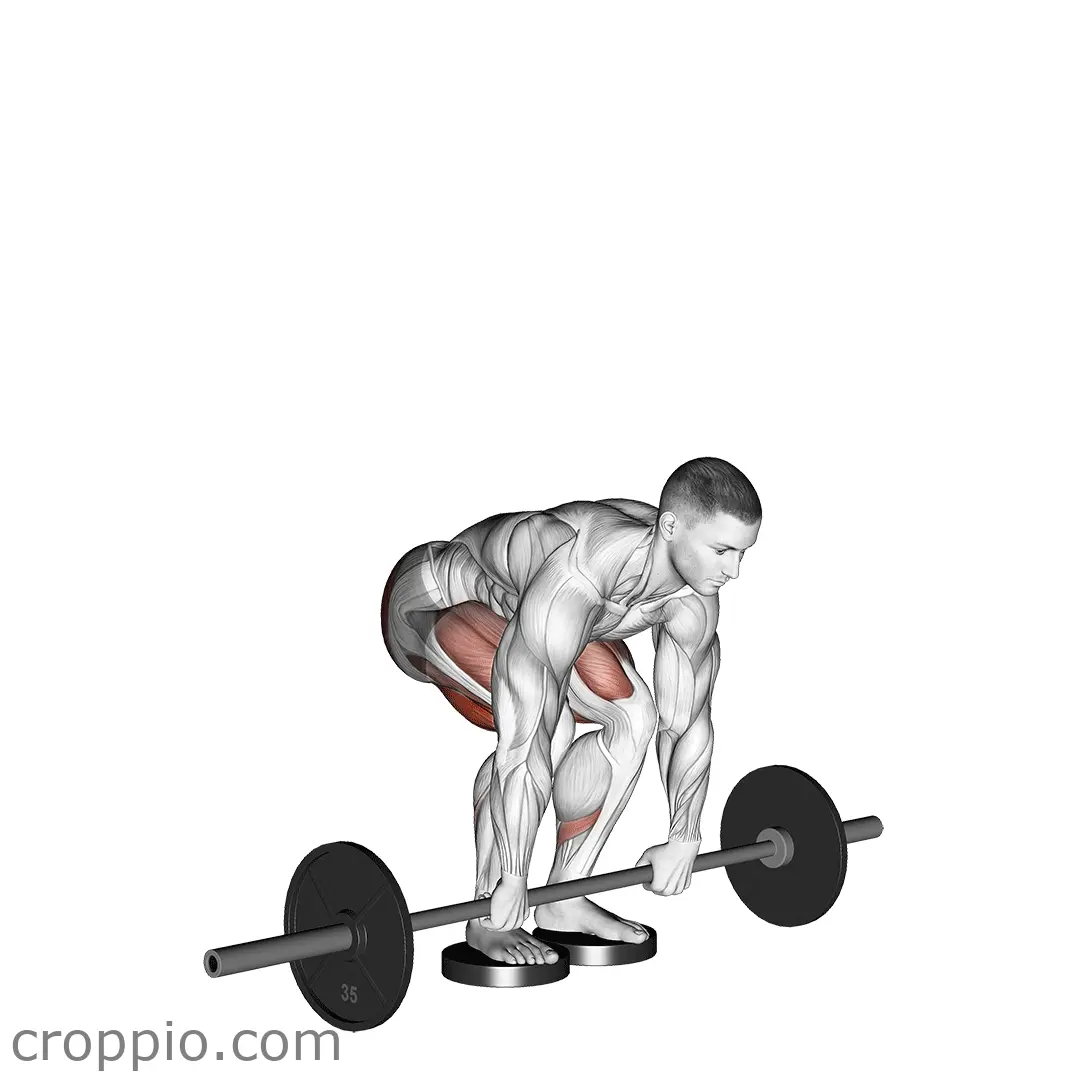
The hex bar deadlift is an effective compound exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. The unique design of the hex bar allows for a more natural lifting position, which engages secondary muscles, including the calves and upper back. The quadriceps are activated as the lifter pushes through their heels, while the hamstrings and glutes support stability and power during the lift. Additionally, the core muscles are engaged to maintain proper posture, making the hex bar deadlift a comprehensive lower-body workout.
Top Mistakes
- Rounded back: Failing to maintain a neutral spine can lead to injury. Always keep your back straight during the lift.
- Incorrect grip: An improper grip can cause instability. Ensure your hands are positioned securely on the handles.
- Excessive forward lean: Leaning too far forward can shift the weight and stress the lower back. Keep your torso upright.
- Uneven weight distribution: Poor balance can lead to dangerous lifting conditions. Make sure to position yourself centrally within the hex bar.
Execution Tips
- Setup: Approach the hex bar and stand in the center with your feet shoulder-width apart. Ensure your toes point slightly outward.
- Grip: Bend at your knees and hips to grasp the handles. Use a neutral grip, with your palms facing your body.
- Posture: Set your shoulders back and down, engage your core, and keep your chest up throughout the movement.
- Lifting phase: Initiate the lift by pushing through your heels. Extend your hips and knees simultaneously, maintaining a straight back.
- Lowering phase: To lower the weight, hinge at your hips first while keeping your back straight, then bend your knees as you descend.
Workouts
The hex bar deadlift can be easily incorporated into a strength training routine. A typical recommendation is to perform 3 to 4 sets of 6 to 10 repetitions, allowing adequate rest periods of 60 to 90 seconds between sets. This exercise pairs well with complementary movements such as squats, lunges, or leg curls, creating a lower-body focused workout. Be sure to adjust your weight according to your experience level, starting lighter as you master your form and technique.
Conclusion
The hex bar deadlift offers a multitude of benefits, combining strength building and functional fitness effectively. Its focus on major muscle groups enhances overall lower-body strength, promotes better posture, and reduces the risk of injury due to its ergonomic design. By incorporating the hex bar deadlift into your workout routine, you can achieve improved athletic performance, stronger core stability, and a balanced physique.