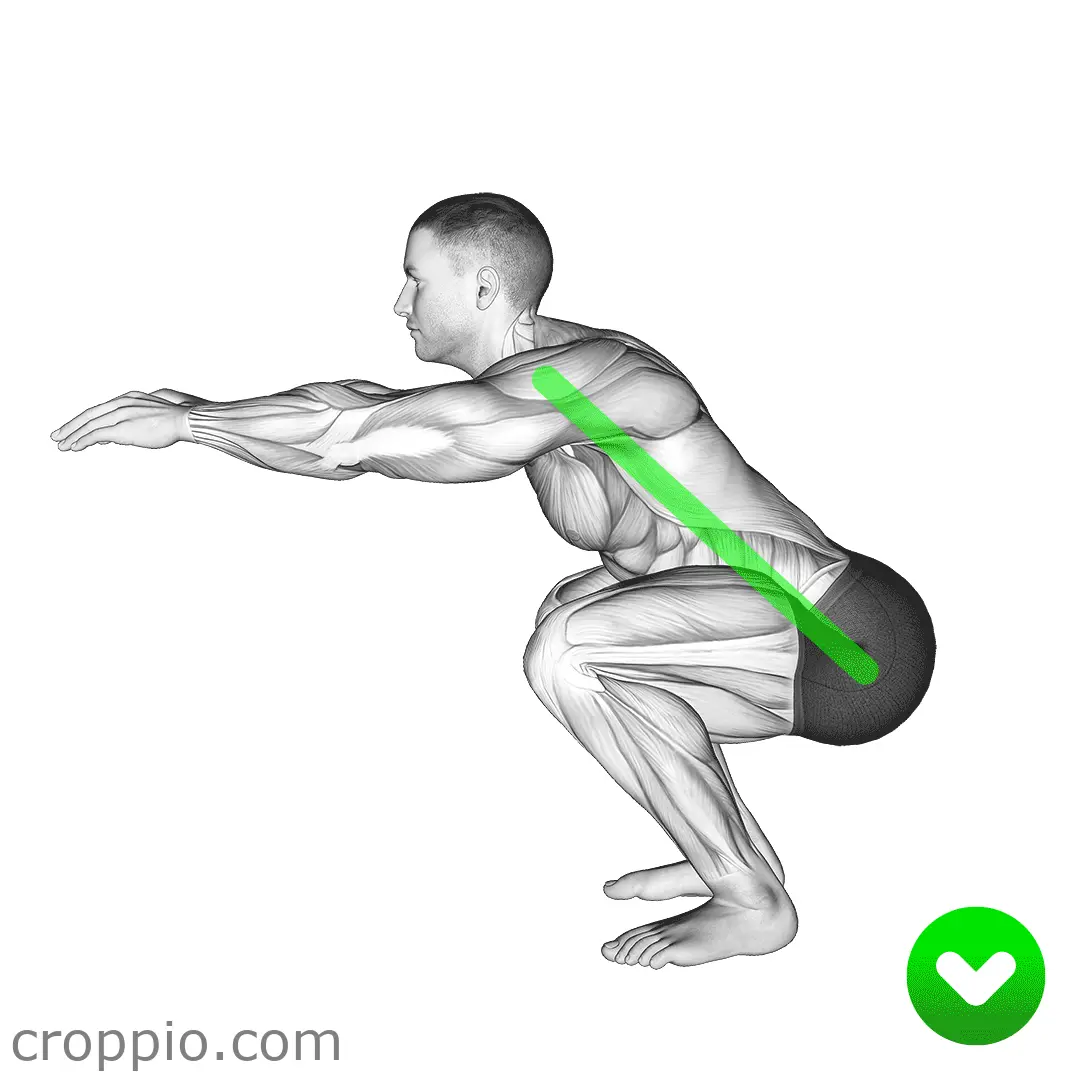
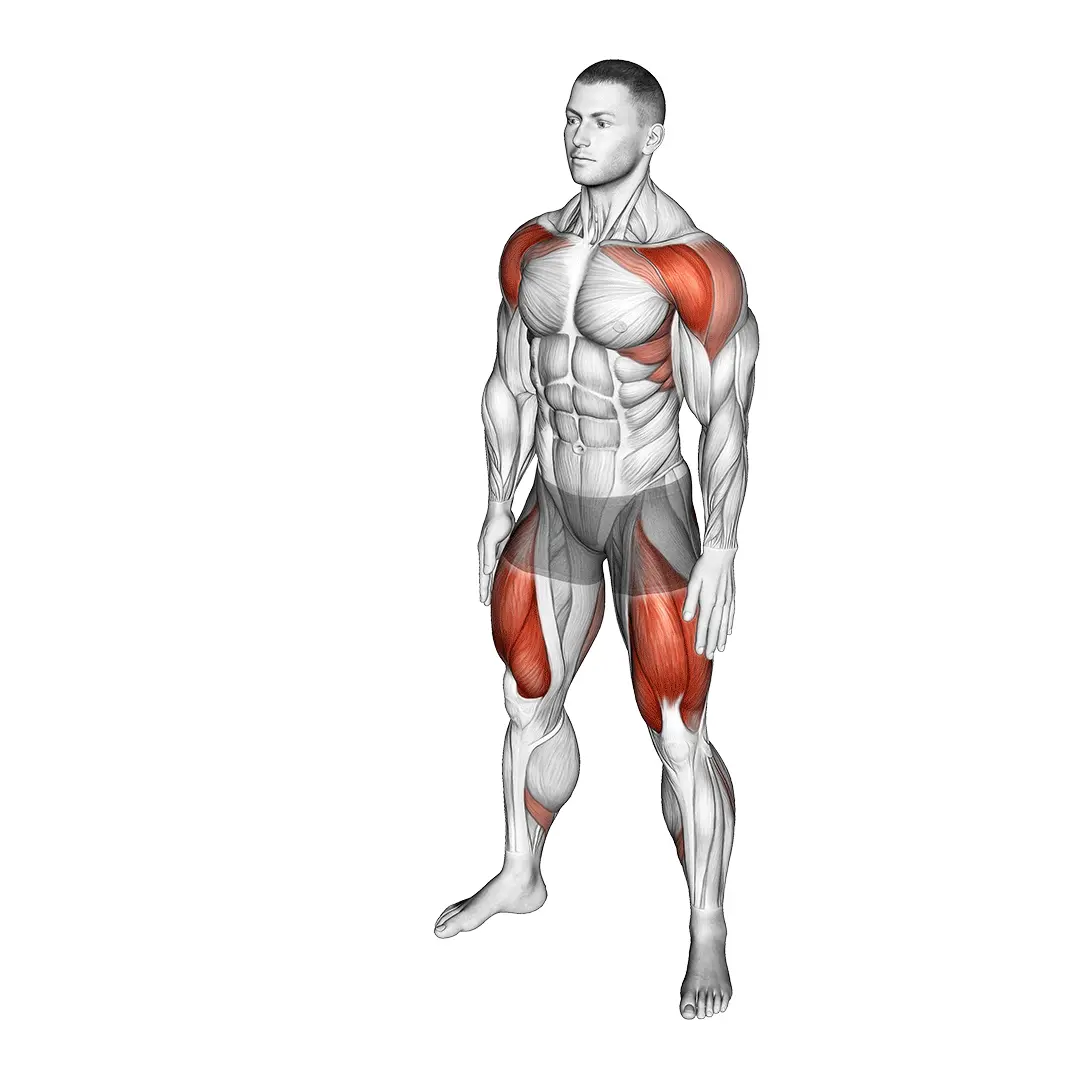
Full Squat Side View
Latest Videos
No videos available.
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
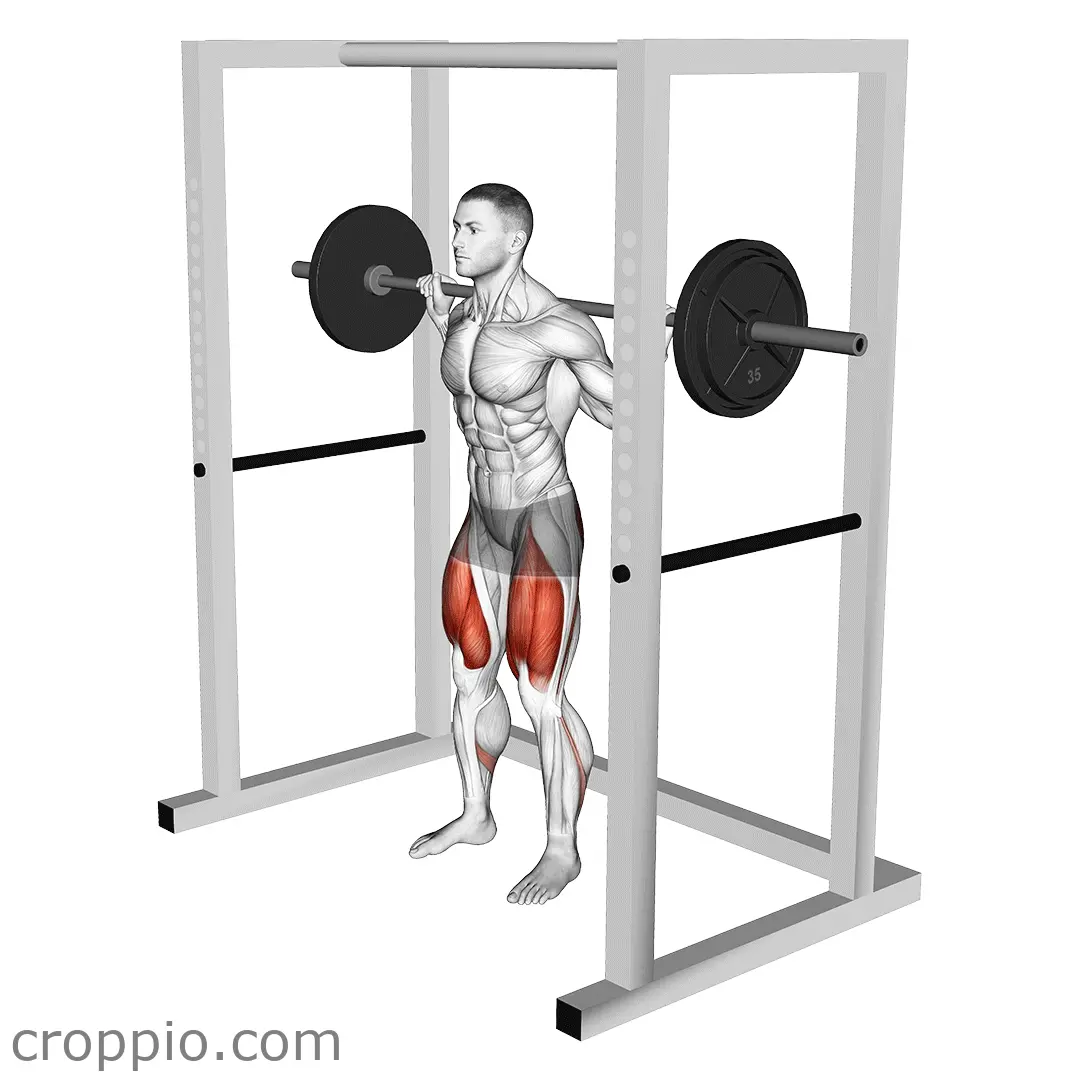
The full squat side view exercise effectively engages several muscle groups, leading to improved strength and stability. The primary muscles targeted include the quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteus maximus. These muscles work in unison during the squat to lower and lift the body. Additionally, the exercise also recruits secondary muscles such as the calves, core, and lower back, which help maintain balance and proper form throughout the movement. Strengthening these muscle groups promotes better athletic performance, joint stability, and functional movement.
Top Mistakes
- Allowing knees to cave in: This can increase the risk of injury and reduce effectiveness.
- Leaning too far forward: This places undue stress on the lower back instead of evenly distributing weight.
- Failing to reach proper depth: Inadequate squats limit muscle engagement and shortchange the benefits of the exercise.
- Not keeping the heels down: Lifting the heels can shift weight to the knees, leading to poor mechanics.
Execution Tips
- Start with feet shoulder-width apart: This provides a stable base and ensures proper alignment.
- Push hips back first: Initiate the squat by sitting back with your hips rather than just bending at the knees.
- Keep chest lifted: Maintain an upright posture by keeping your chest high and shoulders back to avoid rounding the back.
- Go to parallel or below: Aim for your thighs to be at least parallel to the ground to maximize muscle activation.
- Breathe properly: Inhale as you lower into the squat and exhale as you push through the heels to return to standing.
Workouts
The full squat side view can be effectively integrated into a comprehensive workout routine. For strength training, aim for 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 12 repetitions, allowing for sufficient recovery time in between sets. To enhance muscular endurance, consider performing higher repetitions (15-20) with lighter resistance. Complement this exercise with movements that engage the lower body, such as lunges, deadlifts, or leg presses. Incorporating these exercises will provide balanced growth and prevent training plateaus.
Conclusion
The full squat side view is an essential exercise for developing lower body strength and improving overall athletic performance. By targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, this exercise not only builds muscle but also enhances mobility and stability. By avoiding common mistakes and following proper execution tips, individuals can maximize the benefits while minimizing the risk of injury. Incorporating this exercise into a regular workout regimen will contribute greatly to improved physical fitness.