Bodyweight Squat 2
Similar exercises
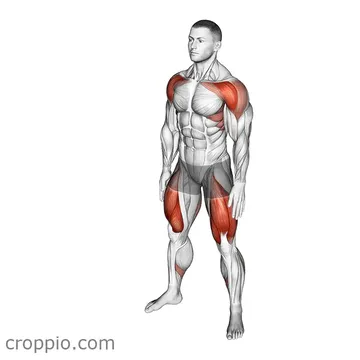
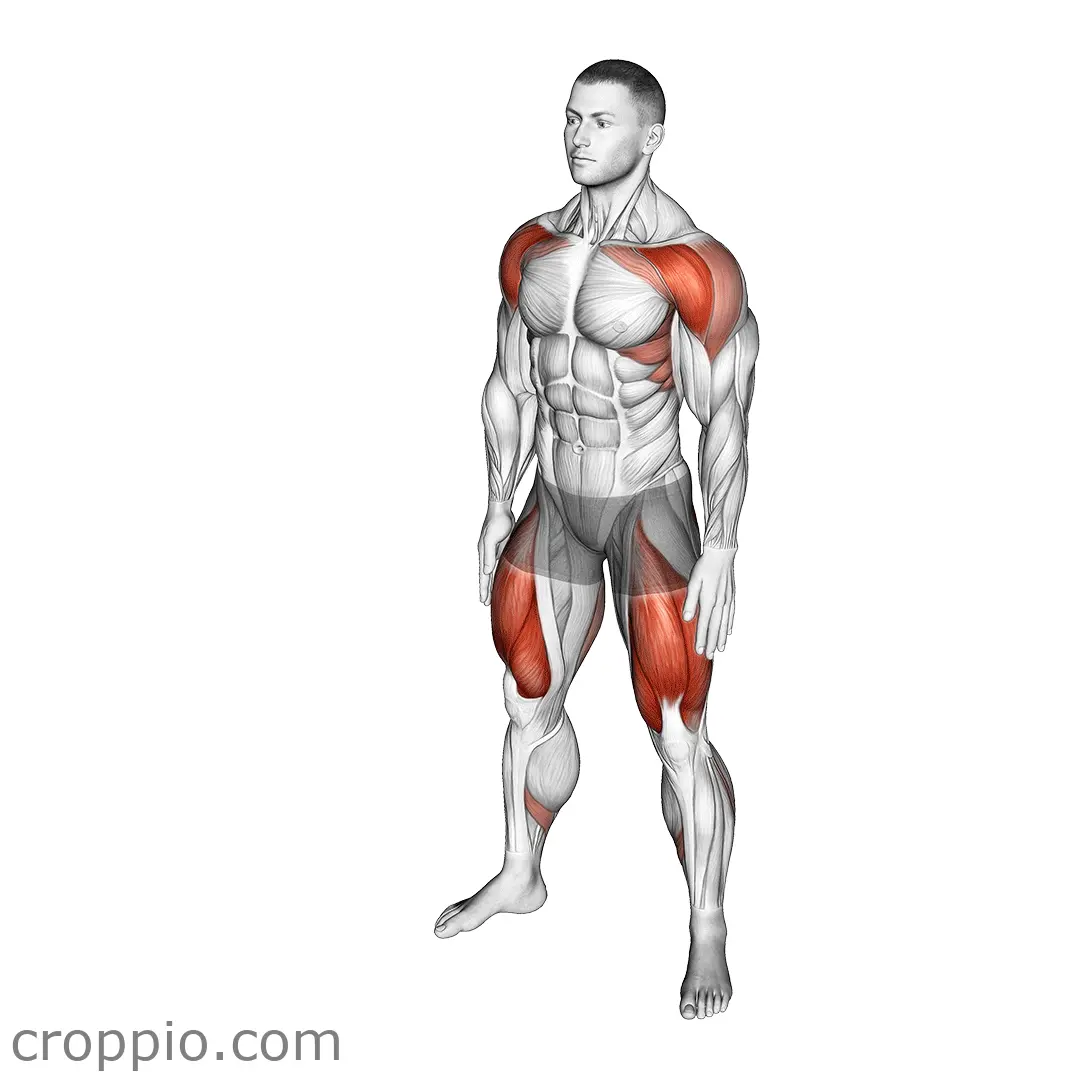
Muscles Involved
The bodyweight squat primarily targets the muscles of the lower body, making it an exceptional compound exercise. The primary muscles engaged include the quadriceps, gluteus maximus, and hamstrings. The quadriceps are responsible for extending the knee as you rise from the squat position, while the glutes power the lift and stabilize the hip joint. The hamstrings assist in controlling the descent and supporting knee flexion.
Additionally, secondary muscles that are engaged during the squat include the calves (gastrocnemius and soleus), hip flexors, and the core muscles, including the abdominals and obliques, which help maintain balance and posture throughout the movement.
Top Mistakes
- Letting the knees cave inward, which can increase the risk of injury and reduce effectiveness.
- Failing to lower the hips sufficiently, resulting in a shallow squat that minimizes muscle engagement.
- Rounding the back or leaning excessively forward, which compromises spinal alignment.
- Not keeping the feet flat on the ground, leading to poor balance and stability during the movement.
Execution Tips
- Start with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes slightly angled outward for better stability.
- Engage your core and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Initiate the squat by pushing your hips back as if sitting into a chair, ensuring that your knees track over your toes.
- Lower your body until your thighs are at least parallel to the ground, then push through your heels to return to standing.
- Keep your gaze ahead and avoid looking down to maintain proper posture.
Workouts
The bodyweight squat can be effectively incorporated into various workout routines. For beginners, aim for 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, focusing on form rather than speed. Intermediate to advanced practitioners can increase the challenge by performing 3-4 sets of 15-20 reps, integrating variations such as pulse squats or jump squats. Pair bodyweight squats with complementary exercises like lunges, plank holds, or glute bridges to create a well-rounded lower body workout.
Conclusion
Bodyweight squats are a versatile and effective exercise that promote lower body strength, stability, and mobility. They engage multiple muscle groups while improving core strength and posture. By mastering proper form and incorporating them into your fitness routine, you can reap the benefits of enhanced athletic performance and overall functional fitness.