Bodyweight Forward Lunge
Latest Videos
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
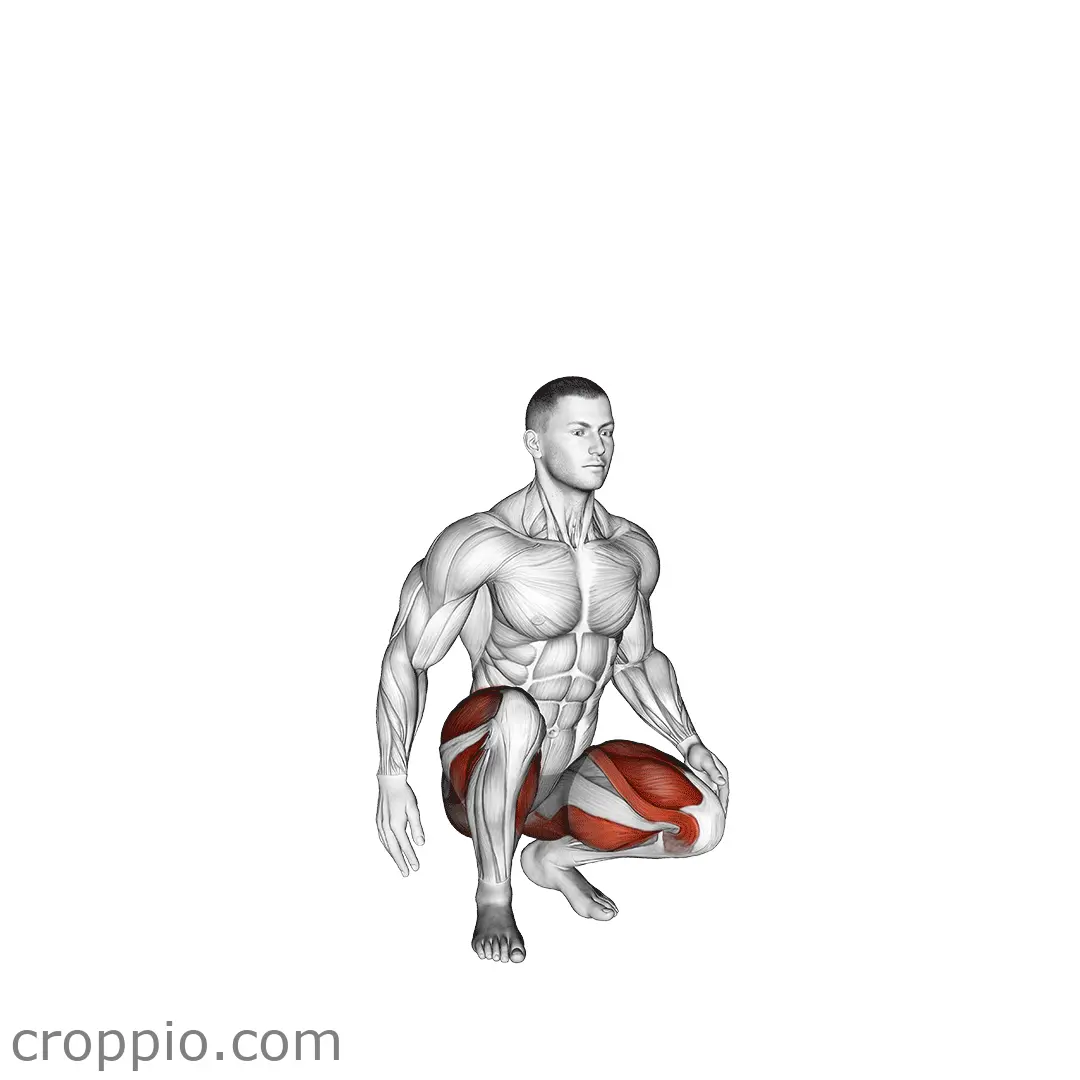
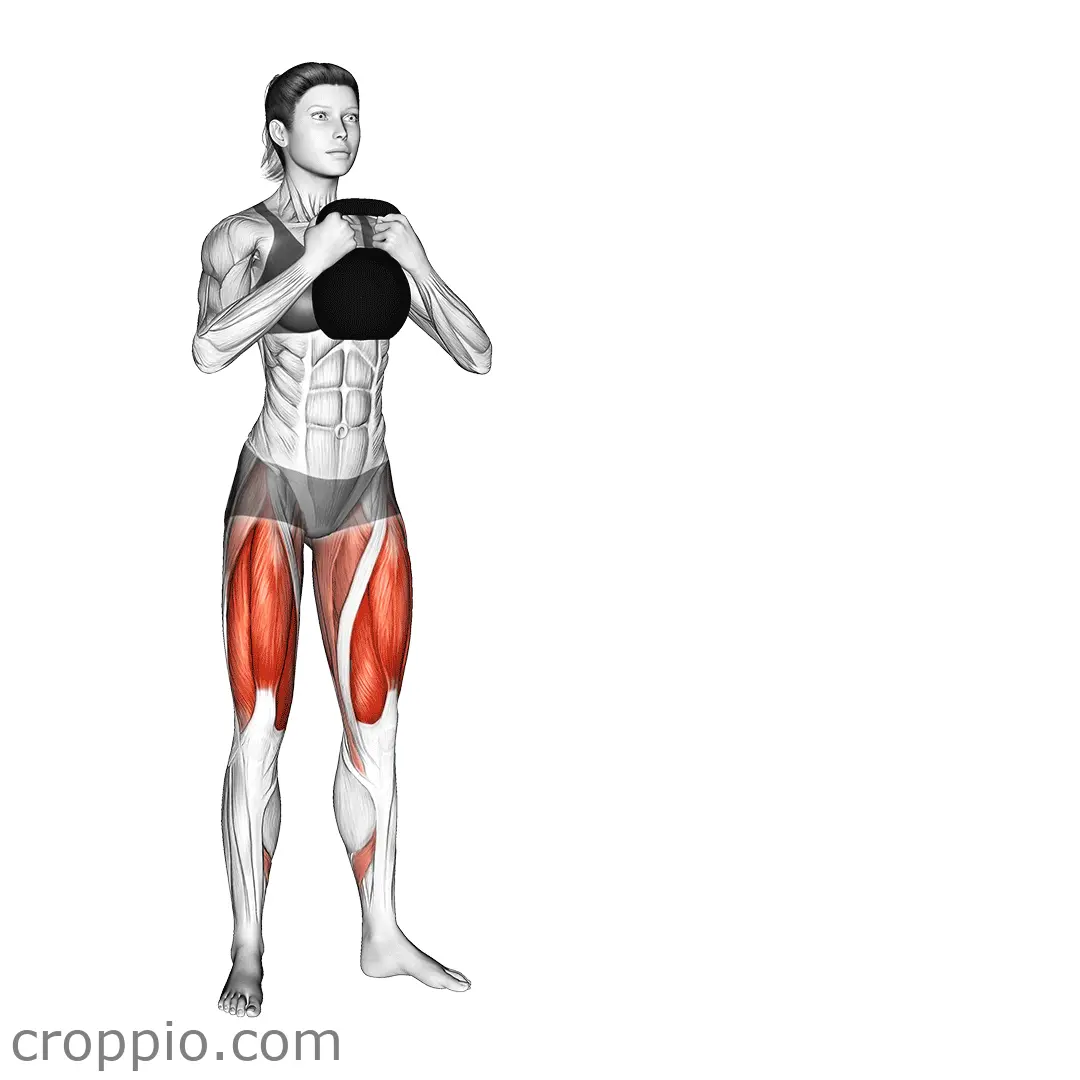
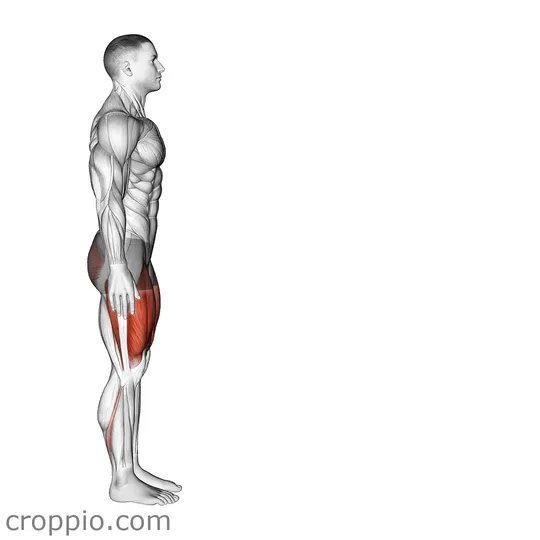
The bodyweight forward lunge is a compound exercise that primarily targets the muscles of the lower body. The major muscles engaged during this movement include:
- Quadriceps: These muscles, located at the front of the thigh, are heavily involved in extending the knee as you push back to the starting position.
- Gluteus Maximust: The largest muscle in the buttocks, the gluteus maximus is activated to stabilize and propel the body forward during the lunge.
- Hamstrings: Positioned at the back of the thigh, the hamstrings assist in controlling the movement and help in stabilizing the knee.
- Calves: The soleus and gastrocnemius muscles in the calf provide support and balance as you lower yourself into the lunge.
- Core Muscles: The abdominals and lower back engage to maintain posture and stability throughout the exercise.
Top Mistakes
- Letting the Knee Go Past the Toes: This can lead to added strain on the knee joint, potentially causing injury.
- Losing Upright Posture: Leaning too far forward compromises balance and effectiveness of the exercise.
- Inconsistent Foot Placement: Not stepping far enough can result in an ineffective lunge, while stepping too far may lead to instability.
Execution Tips
To perform the bodyweight forward lunge correctly, follow these guidelines:
- Stand Tall: Begin in a standing position with feet shoulder-width apart, maintaining a straight back.
- Engage Your Core: Tighten your abdominal muscles to stabilize your pelvis throughout the movement.
- Step Forward: Take a large step forward with one foot, lowering your body until both knees are bent at approximately 90-degree angles.
- Keep Your Weight on Your Front Heel: Ensure your front heel remains flat on the ground while your back knee hovers just above the ground.
- Return Smoothly: Press through your front heel to return to the starting position, and repeat with the opposite leg.
Workouts
The bodyweight forward lunge can be incorporated into various workout routines. A recommended approach would be:
- Sets and Reps: Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions on each leg.
- Complementary Exercises: Pair forward lunges with push-ups or bodyweight squats for a balanced lower and upper body workout.
- Frequency: Include this exercise in your routine 2-3 times per week for optimal strength and conditioning.
Conclusion
The bodyweight forward lunge is a versatile and effective exercise that enhances lower body strength, stability, and core control. By engaging multiple muscle groups, it promotes not only muscle growth but also better functional movement patterns. Regularly incorporating this exercise into your fitness routine can lead to improved athletic performance and a lower risk of injury.