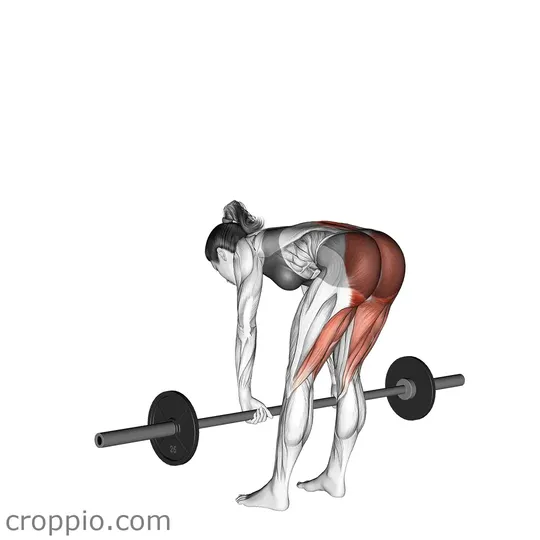
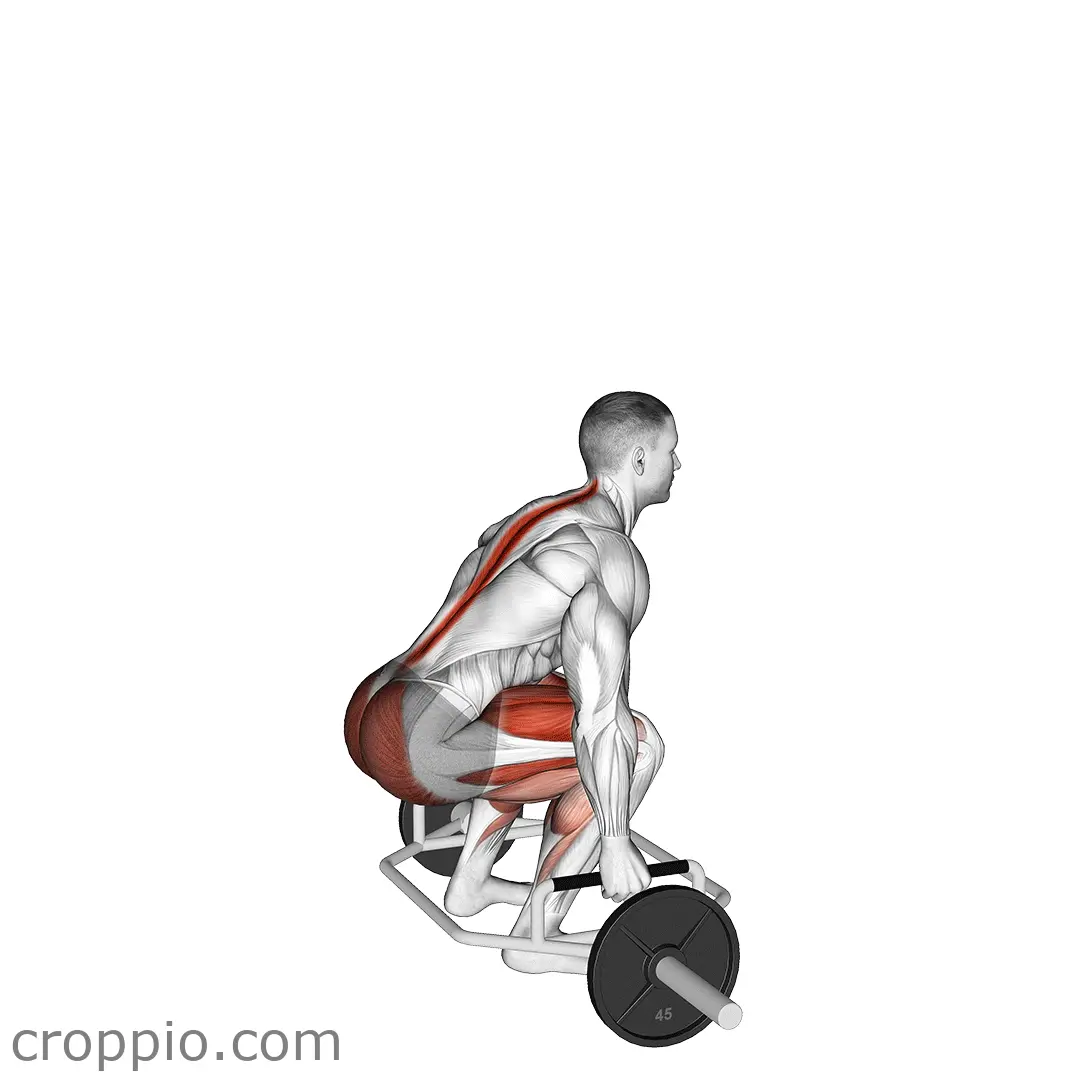
Straight Leg Deadlift
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
The straight leg deadlift primarily targets the hamstrings and gluteus muscles. As you lower the weight, the stretch in the hamstrings is significant. This exercise also engages the lower back through the erector spinae, which helps maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement. Secondary muscles that come into play include the quadriceps, calves, and, to some extent, the upper back muscles, such as the trapezius and rhomboids, which help stabilize the load during the lift.
Top Mistakes
- Rounding the back: This common mistake increases the risk of injury to the spine. Instead, maintain a neutral spine throughout.
- Overextending the knees: Allowing the knees to lock out can place excessive stress on the joints. Keep a slight bend in the knees for safety.
- Using too much weight: Lifting heavy can lead to improper form. Focus on mastering the technique with lighter weights first.
- Failing to engage the core: Neglecting core engagement reduces stability. Always brace your core before performing the lift.
Execution Tips
- Setup: Begin by standing with feet hip-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells in front of your thighs.
- Grip: Use an overhand grip, with your hands positioned slightly wider than shoulder-width.
- Movement: Hinge at the hips while maintaining a slight bend in your knees. Lower the weights towards the ground while keeping your back flat and chest lifted.
- Return: Engage your hamstrings and glutes to pull the weights back up to the starting position by driving your hips forward.
Workouts
The straight leg deadlift can be seamlessly integrated into various workout routines. Aim for 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 12 repetitions, depending on your fitness level and goals. Pair this exercise with complementary movements such as squats or lunges to enhance lower body strength, or incorporate upper body exercises like rows for a balanced workout. Consider using it as part of a leg day routine or a full-body workout to target multiple muscle groups effectively.
Conclusion
The straight leg deadlift is a powerful exercise for building lower body strength, particularly in the hamstrings and glutes. By focusing on proper form and avoiding common mistakes, you can maximize its benefits while minimizing the risk of injury. Regularly incorporating this exercise into your workout routine can improve overall athletic performance, enhance posture, and contribute to injury prevention.