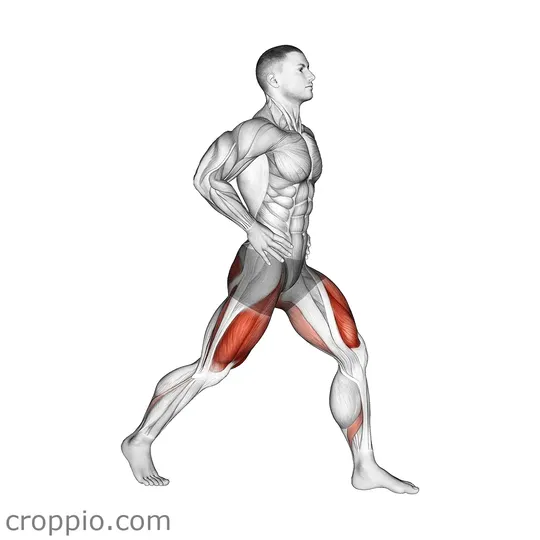
Split Squat

Latest Videos
No videos available.
Split Squat Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
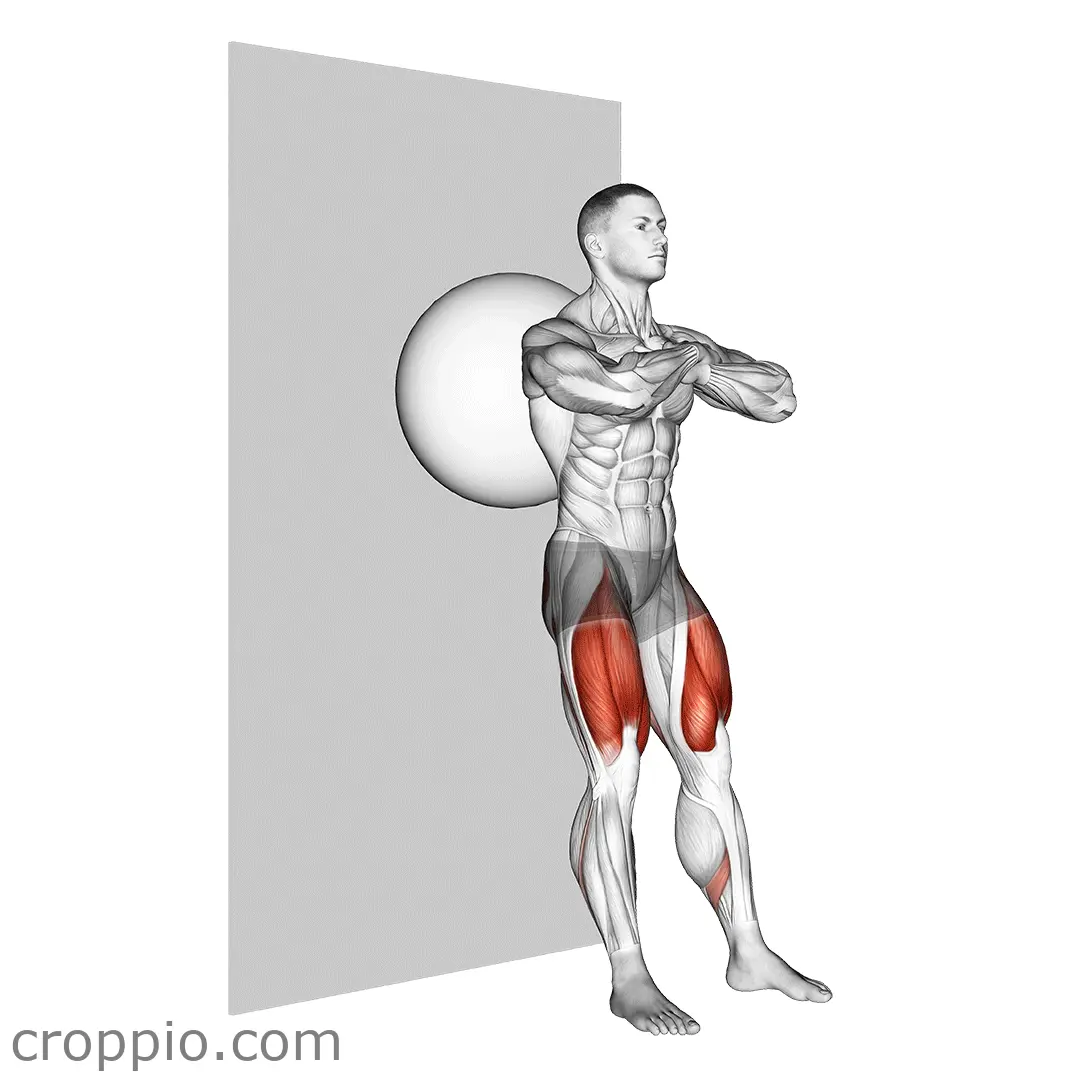
The split squat effectively targets several key muscle groups, making it a valuable addition to any strength training routine. The primary muscles engaged during this exercise are the quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, and calves. The quadriceps work to extend the knee, while the hamstrings play a role in knee flexion and hip extension. Additionally, the glutes are significantly activated as they help stabilize the hips and drive the movement upwards. Secondary muscles include the hip adductors and the core, which assist in maintaining balance and stability throughout the exercise.
Top Mistakes
- Letting the front knee extend beyond the toes, which can increase the risk of injury.
- Failing to maintain an upright torso, leading to poor posture and decreased effectiveness.
- Not engaging the core, which can compromise stability and support.
- Incorrect foot positioning, such as having the back foot too far back or too far forward.
Execution Tips
- Start with your feet hip-width apart, stepping one foot back into a lunge position.
- Ensure that your front knee stays aligned over your ankle and does not cross your toes.
- Keep your torso straight and chest up to maintain proper posture throughout the movement.
- Lower your hips until your back knee hovers just above the ground, then push through your front foot to return to the starting position.
- For added difficulty, hold weights in each hand or try incorporating a front rack or overhead position.
Workouts
The split squat can be incorporated into various workout routines to enhance strength and stability. For beginners, starting with 3 sets of 8-10 repetitions on each leg is recommended. As you progress, you can increase the number of sets to 4 and the repetitions to 12-15. Integrating complementary exercises such as lunges, step-ups, or single-leg deadlifts can create a well-rounded lower body workout. Additionally, combining split squats with upper body exercises like push-ups or dumbbell rows allows for a full-body routine that maintains engagement and balance.
Conclusion
The split squat is a highly effective exercise for developing lower body strength, balance, and stability. By engaging multiple muscle groups, it helps enhance athletic performance and improve functional movements necessary in daily life. Its versatility and adaptability make it suitable for individuals at all fitness levels, providing a solid foundation for advancing to more complex movements.