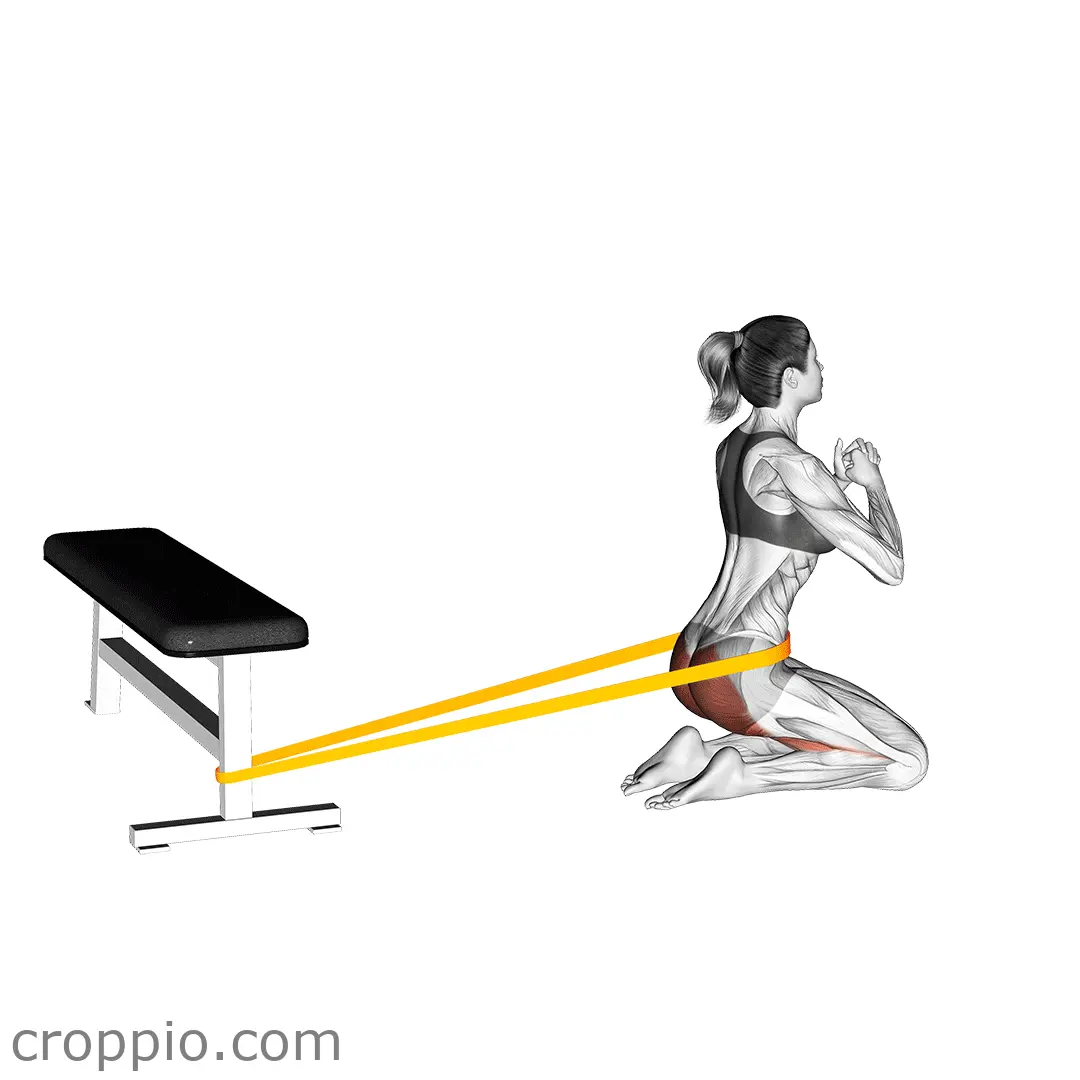
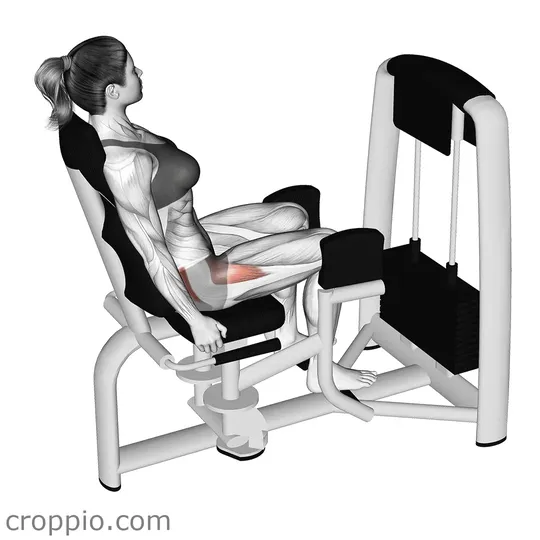
Seated Hip Abduction
Latest Videos
No videos available.
Seated Hip Abduction Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
The seated hip abduction exercise primarily targets the hip abductor muscles, which include the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. These muscles play a crucial role in stabilizing the pelvis during various movements and activities such as walking, running, and jumping. The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) also assists in this exercise, contributing to the effective movement of the hip joint. Secondary muscles involved include the quadratus lumborum and some muscles of the lower back, which help maintain proper posture and spine alignment while performing the exercise.
Top Mistakes
- Not keeping the back straight: Letting the back slouch can lead to poor form and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Using excessive weight: Choosing too heavy a resistance can strain the hip muscles and joints, making proper execution difficult.
- Allowing legs to drop back: Instead of maintaining controlled movement, dropping the legs back can detract from targeting the hip abductors effectively.
- Holding breath: Failing to breathe properly can create tension and hinder performance.
Execution Tips
- Start seated on a bench or chair with your back straight and feet flat on the ground, hip-width apart.
- Adjust the resistance band or weights so that they provide a challenge, but maintain a comfortable range of motion.
- Engage your core muscles for stability, keeping the pelvic area stable throughout the movement.
- Perform the movement by slowly lifting one leg out to the side while keeping the other leg steady, ensuring the motion is controlled.
- Hold the position for a moment at the peak of the movement before lowering the leg back to the starting position.
- Breathe steadily; exhale as you lift your leg and inhale as you lower it back.
Workouts
Incorporating seated hip abduction into your workout routine is simple. Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 reps for each leg, gradually increasing resistance as you get stronger. This exercise can be complemented with additional lower body exercises such as squats, lunges, and glute bridges to achieve a balanced workout, targeting all areas of the legs and glutes effectively. Be sure to include warm-up and cool-down stretches to maintain flexibility and prevent injury.
Conclusion
The seated hip abduction exercise is an excellent addition to any fitness routine. It effectively strengthens the hip abductors, enhances stability, and aids in the prevention of injuries by improving balance and coordination. Regularly performing this exercise can contribute to better athletic performance and overall functional movement, making it an essential exercise for anyone looking to enhance their lower body strength.