Push Up Handles
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
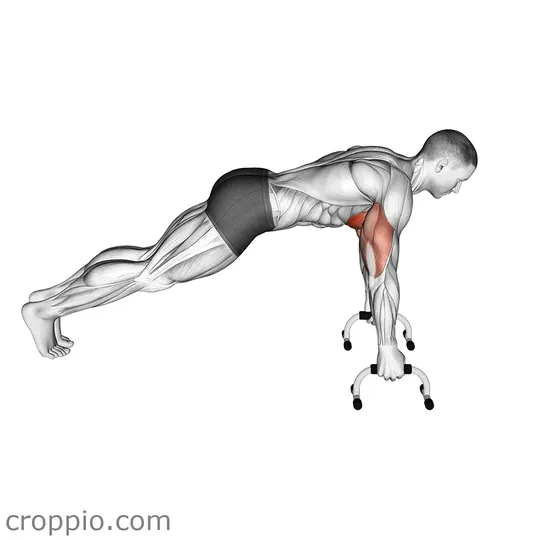
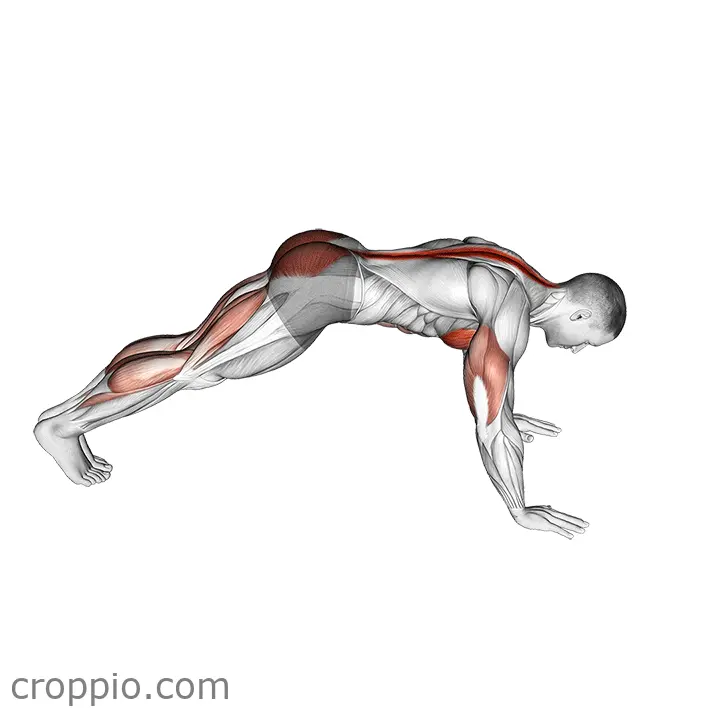
The push-up handles exercise primarily targets the pectoralis major, the large muscle in the chest, as well as the triceps brachii located on the back of the upper arm. These muscles work in unison to push the body away from the ground. Secondary muscles involved include the deltoids (shoulders), the serratus anterior (located on the sides of the thorax), and the core muscles, which stabilize the body during the movement. Utilizing handles can enhance muscle engagement and improve form, making push-ups more effective for overall upper body strength.
Top Mistakes
- Neglecting to maintain a neutral spine, leading to lower back strain.
- Allowing elbows to flare out excessively, reducing efficiency and increasing injury risk.
- Not using the handles properly, which can create an unstable surface and hinder performance.
- Failing to engage the core, which contributes to a sagging or elevated body position.
Execution Tips
- Begin in a plank position with the handles placed shoulder-width apart and your hands firmly gripping them.
- Align your body in a straight line from head to heels; avoid arching or sagging your back.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows while keeping them at a 45-degree angle to your torso.
- Push back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms without locking your elbows.
- Focus on engaging your core throughout the movement to maintain stability.
Workouts
The push-up handle exercise can be easily integrated into a comprehensive workout routine. A typical set might consist of 3 groups of 8–12 repetitions, with a 60-90 second rest between sets for optimal recovery. For variety, you can mix push-up handles with other upper body and core exercises such as dumbbell rows, planks, or dips. Additionally, performing supersets (consecutive exercises without rest) with complementary movements will maximize your workout intensity and muscle building.
Conclusion
Incorporating push-up handles into your fitness routine not only enhances strength and muscle development in the upper body but also encourages proper form and stability. This exercise provides a versatile option for beginners and advanced fitness enthusiasts alike, helping to improve overall performance, posture, and functional movement patterns. Regular practice can lead to noticeable improvements in strength and endurance, making it a worthwhile addition to any workout regimen.