Power Lunge Movement
Power Lunge Movement Workouts
Similar exercises
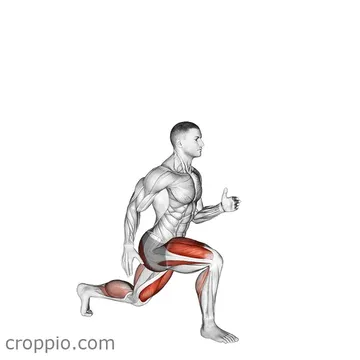
Muscles Involved
The power lunge movement is an explosive lower body exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. When you extend and push from your back foot, the quadriceps engage strongly to propel your body forward, while the glutes help stabilize and power the movement. Additionally, the hamstrings play a crucial role in decelerating your body, providing balance and support throughout the exercise. Secondary muscles engaged include the calves and core muscles; the calves stabilize the ankle during the movement, and the core works to maintain overall stability and posture.
Top Mistakes
- Failing to maintain proper knee alignment: The front knee should not extend beyond the toes to avoid unnecessary strain on the joint.
- Neglecting to engage the core: A loose core can lead to poor balance and an ineffective movement.
- Performing the movement too quickly: Rushing through the lunge can lead to improper form and increase the risk of injury.
- Inadequate depth in the lunge: Not lowering the back knee close to the ground limits the exercise's benefits.
Execution Tips
- Start by positioning your feet shoulder-width apart; take a step back with one foot to initiate the lunge.
- Ensure to bend both knees to about a 90-degree angle while keeping the front knee aligned with the ankle.
- Engage your core throughout the movement for stability and balance.
- Push through the heel of your front foot and the ball of your back foot as you return to the starting position.
- Gradually increase the pace as you become more comfortable with the technique; aim for a smooth, controlled motion.
Workouts
The power lunge can easily be incorporated into various workout routines. Aim for 3 to 4 sets of 10 to 15 repetitions per leg, allowing for 30 seconds of rest between sets. For a comprehensive lower body workout, pair the power lunge with exercises like squats, deadlifts, and calf raises. Alternatively, incorporate it into a circuit with cardio elements, such as burpees or jump squats, to boost intensity and heart rate.
Conclusion
The power lunge movement offers numerous benefits, including improved strength, flexibility, and coordination of the lower body muscles. Its dynamic nature not only enhances muscle engagement but also elevates the heart rate, contributing to cardiovascular fitness. By incorporating this exercise into your workout routine, you can achieve a more toned lower body while also developing functional strength that translates to everyday activities.