Half Knee Bend Squat 1
Half Knee Bend Squat 1 Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
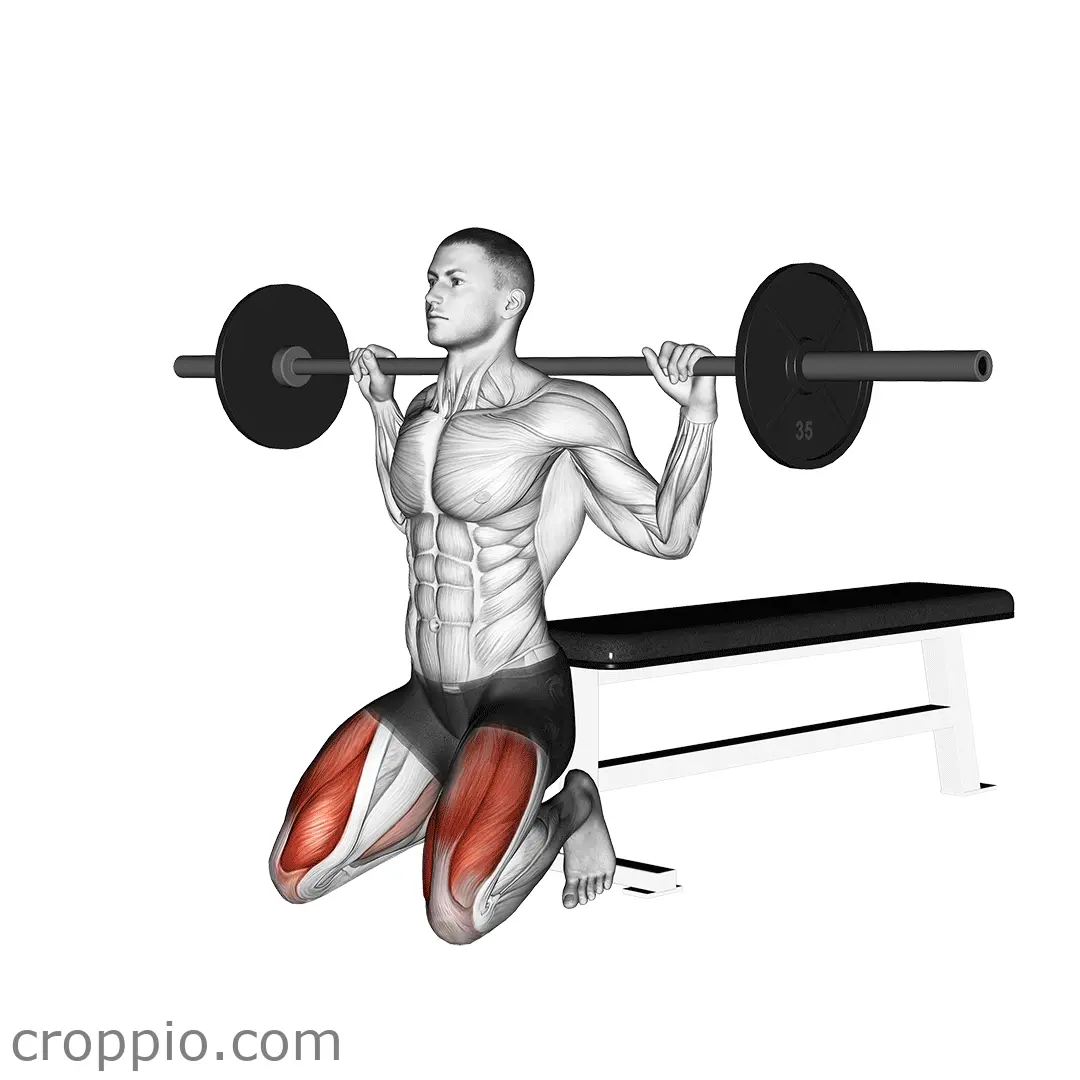
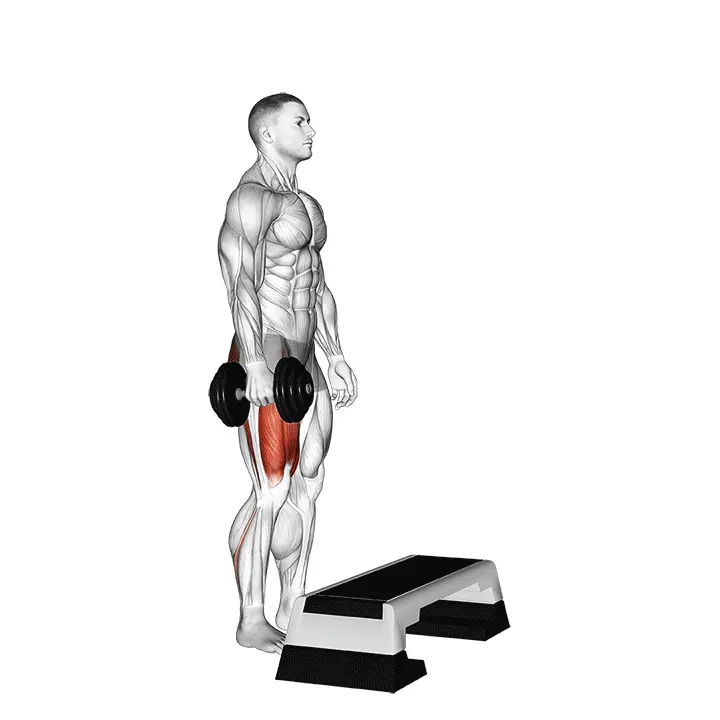
The half knee bend squat 1 is an effective lower body exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps muscle group located at the front of your thighs. This exercise also engages the hamstrings and glutes as secondary muscles, creating balanced development throughout the legs. Additionally, your core muscles, including the abdominals and lower back, are activated to maintain stability and support during the movement.
Top Mistakes
- Not Squatting Low Enough: Many individuals do not lower themselves enough into the squat, which reduces the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Failing to Keep Knees Aligned: Allowing the knees to cave inwards during the squat can lead to injury and improper muscle engagement.
- Incorrect Foot Placement: Placing feet too close or too far apart can cause instability and poor form.
- Leaning Forward: Hunching over rather than maintaining an upright torso can strain the back and diminish the squat's benefits.
Execution Tips
- Starting Position: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes slightly pointed outward. Engage your core.
- Performing the Squat: Initiate the movement by bending at the hips and knees, ensuring your weight is evenly distributed across your feet. Aim to squat until your thighs are at a 45-degree angle or parallel to the ground.
- Knees and Back Alignment: Keep your knees in line with your toes throughout the movement, and maintain a neutral spine.
- Return to Start: Pushing through your heels, return to the starting position while continuing to keep your chest up and core engaged.
Workouts
The half knee bend squat 1 can be easily incorporated into a workout routine as part of a strength training program. It is recommended to perform 3 sets of 10 to 15 repetitions, with 60-90 seconds rest between sets. For a comprehensive lower body workout, combine this exercise with lunges, leg presses, and calf raises to target various muscle groups effectively.
Conclusion
Incorporating the half knee bend squat 1 into your fitness regime offers numerous benefits, including enhanced lower body strength, improved balance, and core stability. This exercise not only aids in muscle development but also promotes better posture and functional movement patterns, making it a valuable addition to any workout plan.