Full Sit Up
Full Sit Up Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
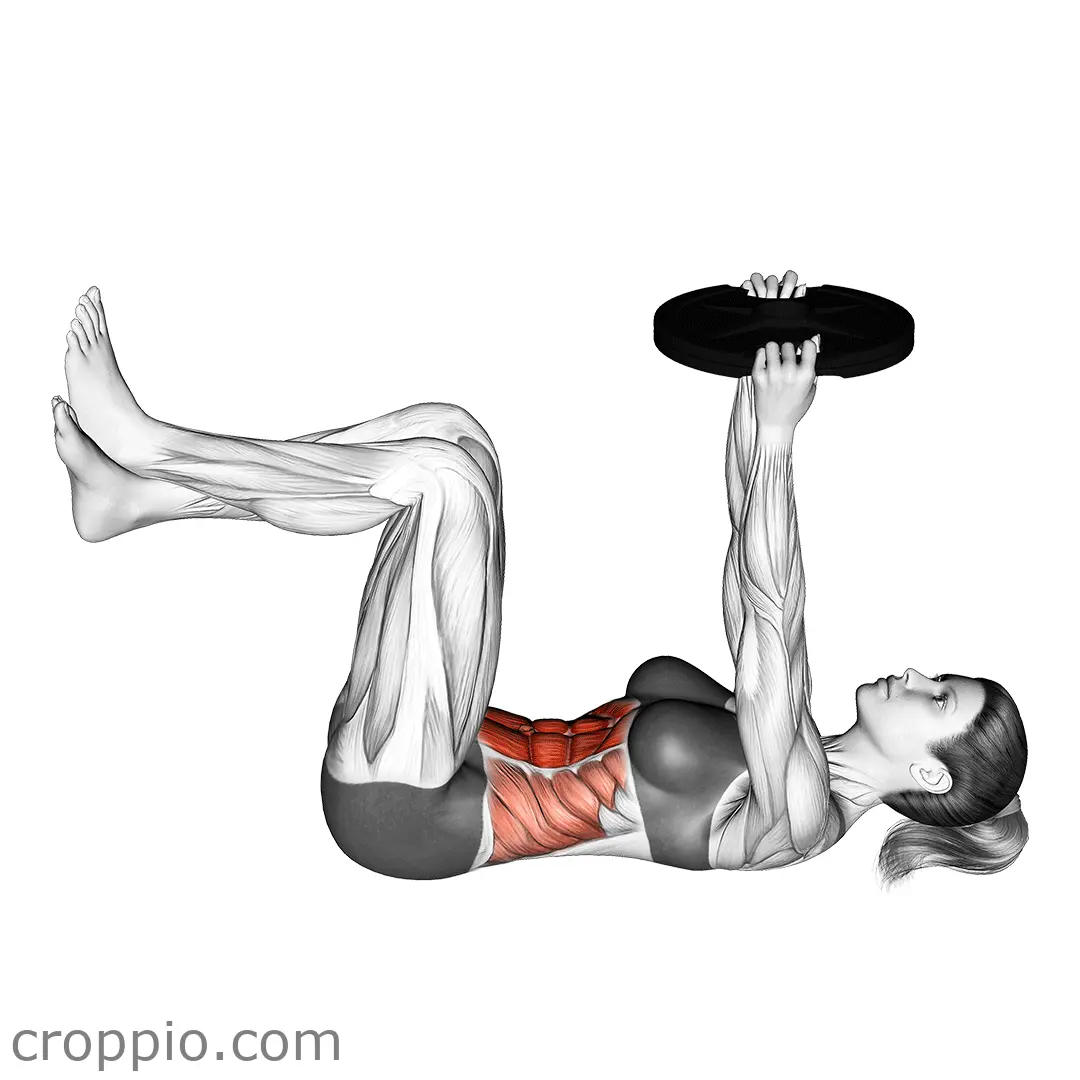
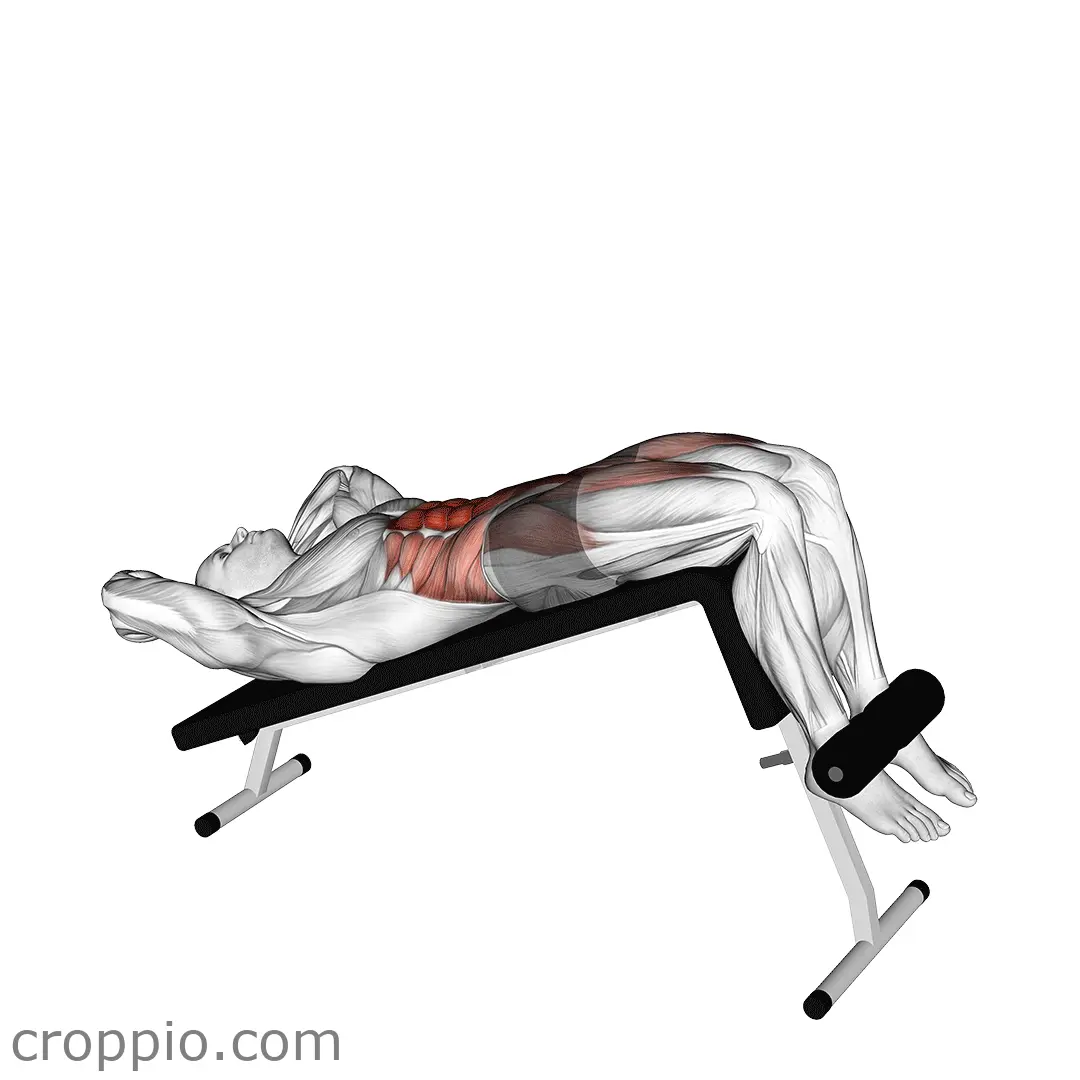
The full sit-up is a compound exercise that primarily targets the abdominal muscles, particularly the rectus abdominis, which is the muscle responsible for the "six-pack" appearance. In addition to the rectus abdominis, full sit-ups also engage the hip flexors, specifically the iliopsoas and rectus femoris. Secondary muscles include the obliques, as they assist in stabilizing the torso during the movement, and the chest and neck muscles, which help to facilitate the lifting motion.
Top Mistakes
- Rounding the back: Lifting the upper body while allowing the back to round can cause strain.
- Pulling on the neck: Using the hands to yank the head or neck forward can lead to injury.
- Using momentum: Engaging in fast or jerky movements instead of controlled motion compromises effectiveness.
- Incomplete range of motion: Not fully lowering or raising the torso leads to limited core activation.
Execution Tips
- Start from a supine position: Lie flat on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground, hip-width apart.
- Place your hands behind your head: Ensure your elbows are wide and avoid pulling your head forward during the lift.
- Engage your core: Tighten your abdominal muscles before initiating the sit-up.
- Move slowly and control: Curl your torso up toward your thighs, maintaining a flat back and avoiding momentum.
- Lower with control: Return to the starting position slowly, ensuring the lower back remains in contact with the ground.
Workouts
Incorporating full sit-ups into your workout routine can effectively strengthen the core. A recommended structure could involve performing 3 sets of 12-15 repetitions. To maximize benefits, consider pairing full sit-ups with complementary exercises such as planks, leg raises, or Russian twists. Additionally, incorporating variations, like weighted sit-ups or decline sit-ups, can enhance difficulty and stimulate further muscle growth.
Conclusion
The full sit-up is an effective exercise for building core strength, improving muscular endurance, and enhancing overall stability. By engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously, this exercise contributes significantly to a well-rounded fitness regimen. However, focusing on proper form and avoiding common mistakes is essential to maximize its benefits while minimizing the risk of injury.