Elbow Extension Biomechanic
Latest Videos
No videos available.
Elbow Extension Biomechanic Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
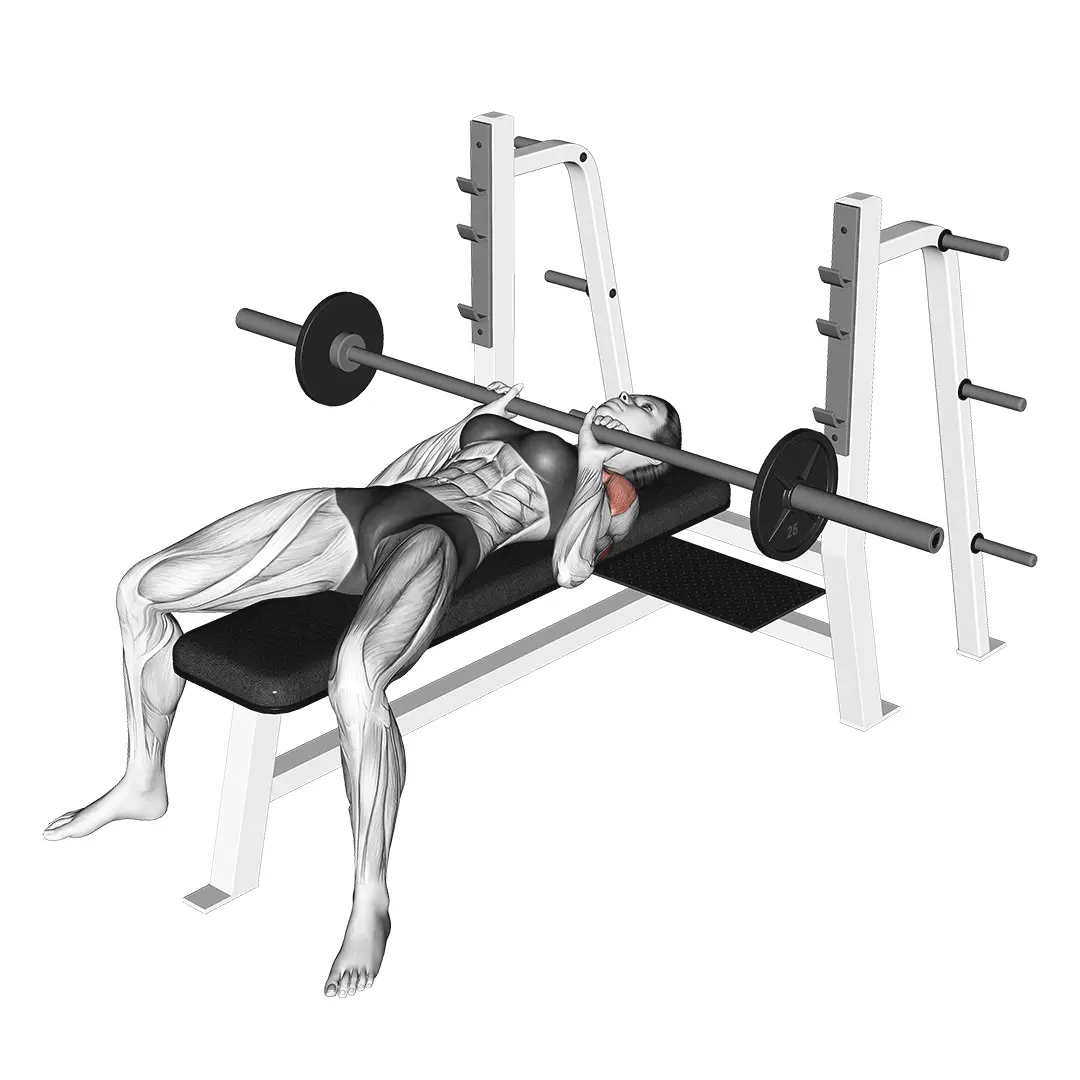
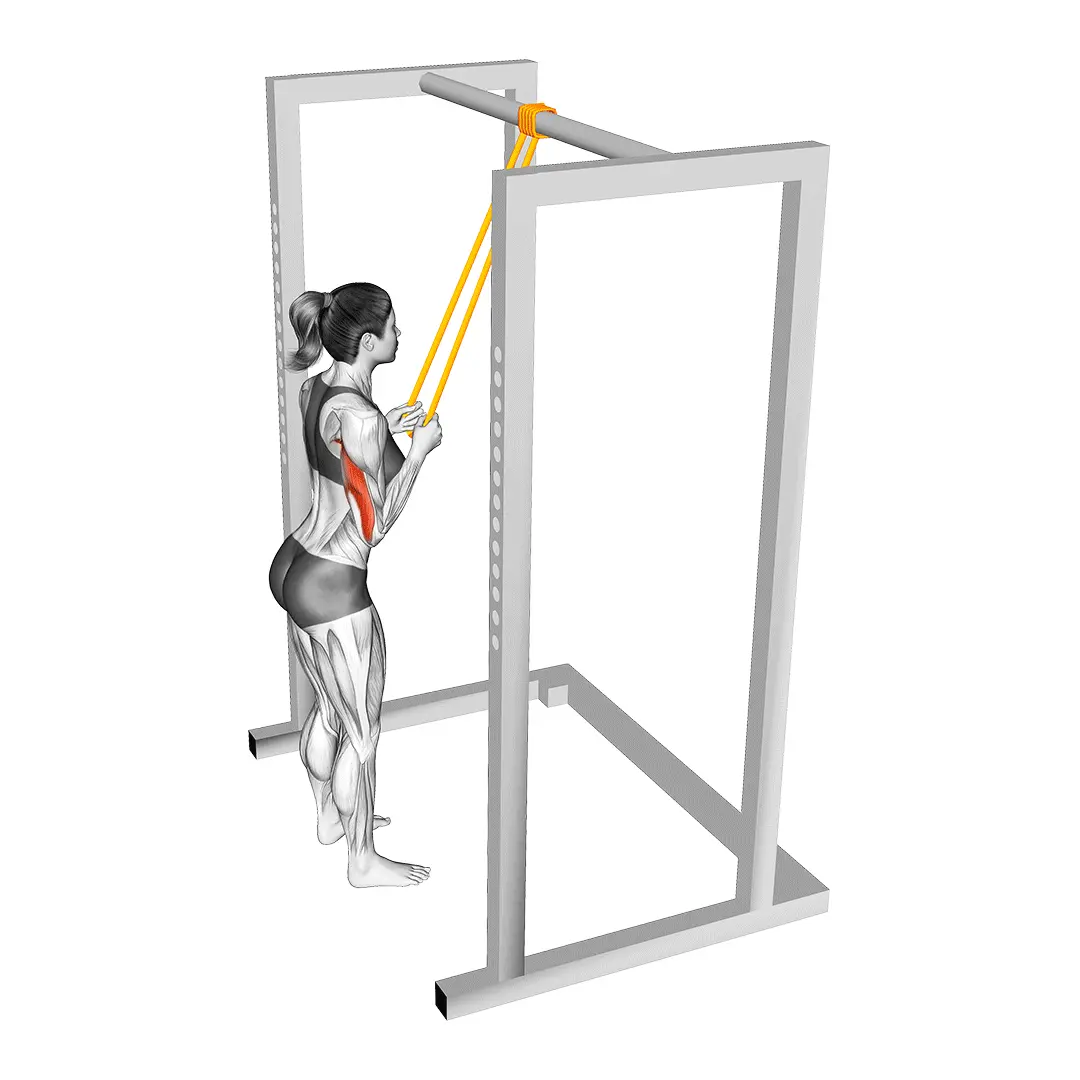
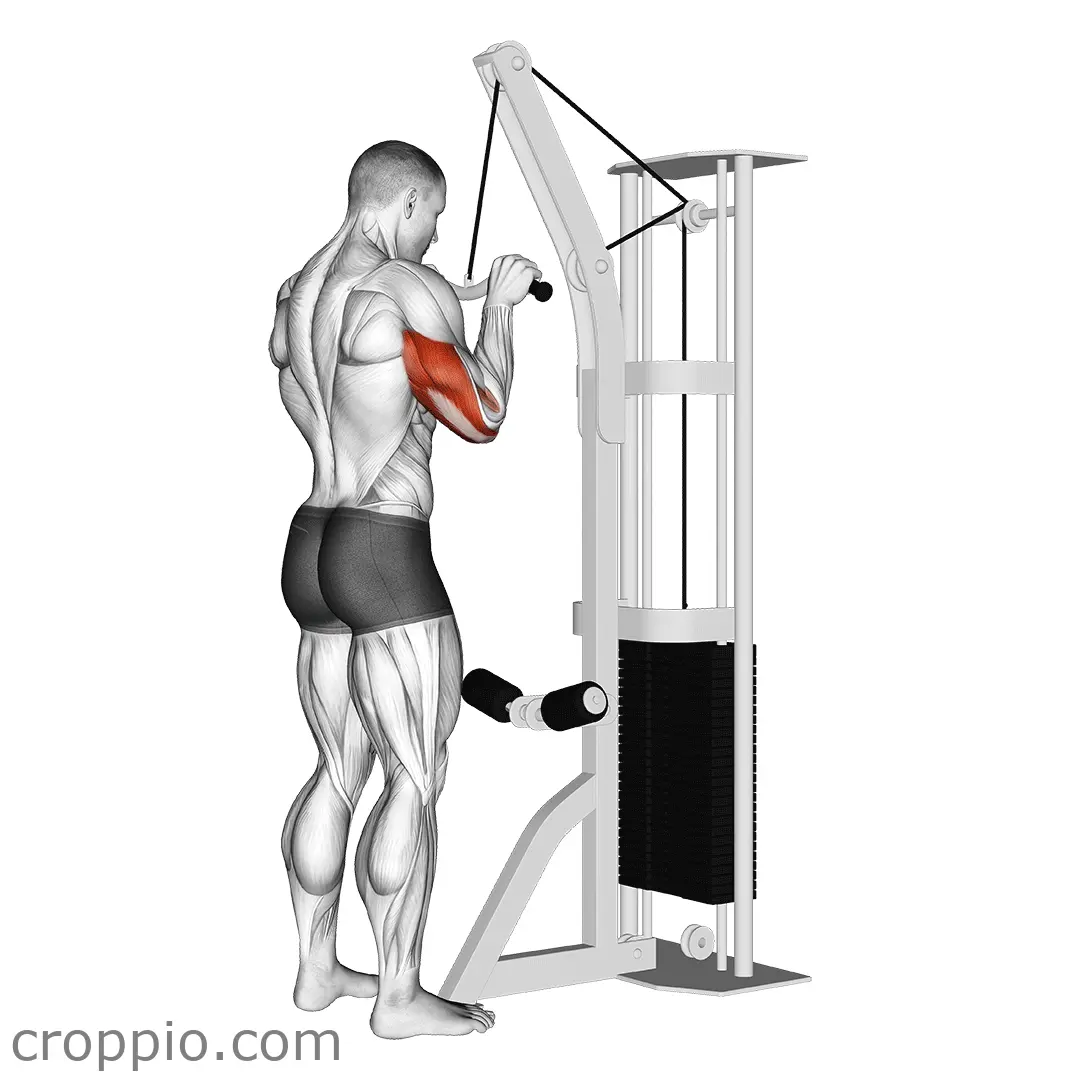
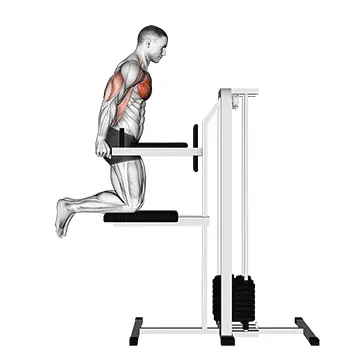
The elbow extension biomechanic primarily targets the triceps brachii muscle, which is responsible for extending the elbow joint. This muscle consists of three heads: the long head, lateral head, and medial head, all contributing to the extension motion. Secondary muscles involved in this movement include the anconeus, a small muscle located at the elbow that assists with extension, as well as the shoulder stability muscles like the deltoids and rotator cuff, which can play a supportive role during various variations of the exercise.
Top Mistakes
- Allowing the elbows to flare out excessively can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase strain on the shoulder.
- Using momentum rather than controlled movement to lift the weights can lead to improper engagement of the triceps and increase the risk of injury.
- Neglecting full elbow extension and stopping short can hinder muscle growth and strength development.
- Incorrect grip width on a cable machine or barbell, which can affect muscle activation and put unnecessary stress on the wrists.
Execution Tips
- Start with a moderate weight to ensure you can maintain proper form throughout the exercise.
- Keep your elbows close to your body and focus on squeezing the triceps at the top of the movement.
- Maintain a neutral spine and engage your core throughout to support your posture.
- Perform the movement slowly and under control, taking care to extend and flex the elbows fully with each repetition.
Workouts
The elbow extension biomechanic can be effectively integrated into both upper body and complete strength training routines. A recommended approach would involve performing 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions. Pair this exercise with complementary movements such as bench presses, push-ups, or overhead presses to engage other muscle groups and maintain balance in your workout. Be sure to include adequate rest periods of 60-90 seconds between sets for optimal recovery.
Conclusion
The elbow extension biomechanic is a fundamental exercise that primarily strengthens the triceps while promoting shoulder stability and overall upper body strength. Incorporating this exercise into your routine can enhance muscle tone, improve athletic performance, and assist in functional movements that require elbow extension. By focusing on proper technique and avoiding common mistakes, you can maximize the benefits and minimize the risk of injury, making it a valuable addition to your fitness regimen.