Chest Squeeze
Latest Videos
No videos available.
Chest Squeeze Workouts
Similar exercises
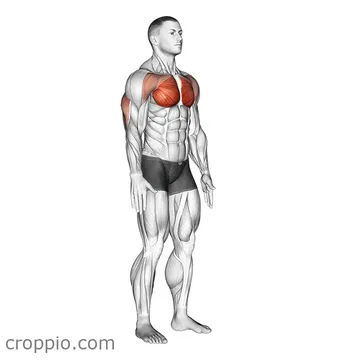
Muscles Involved
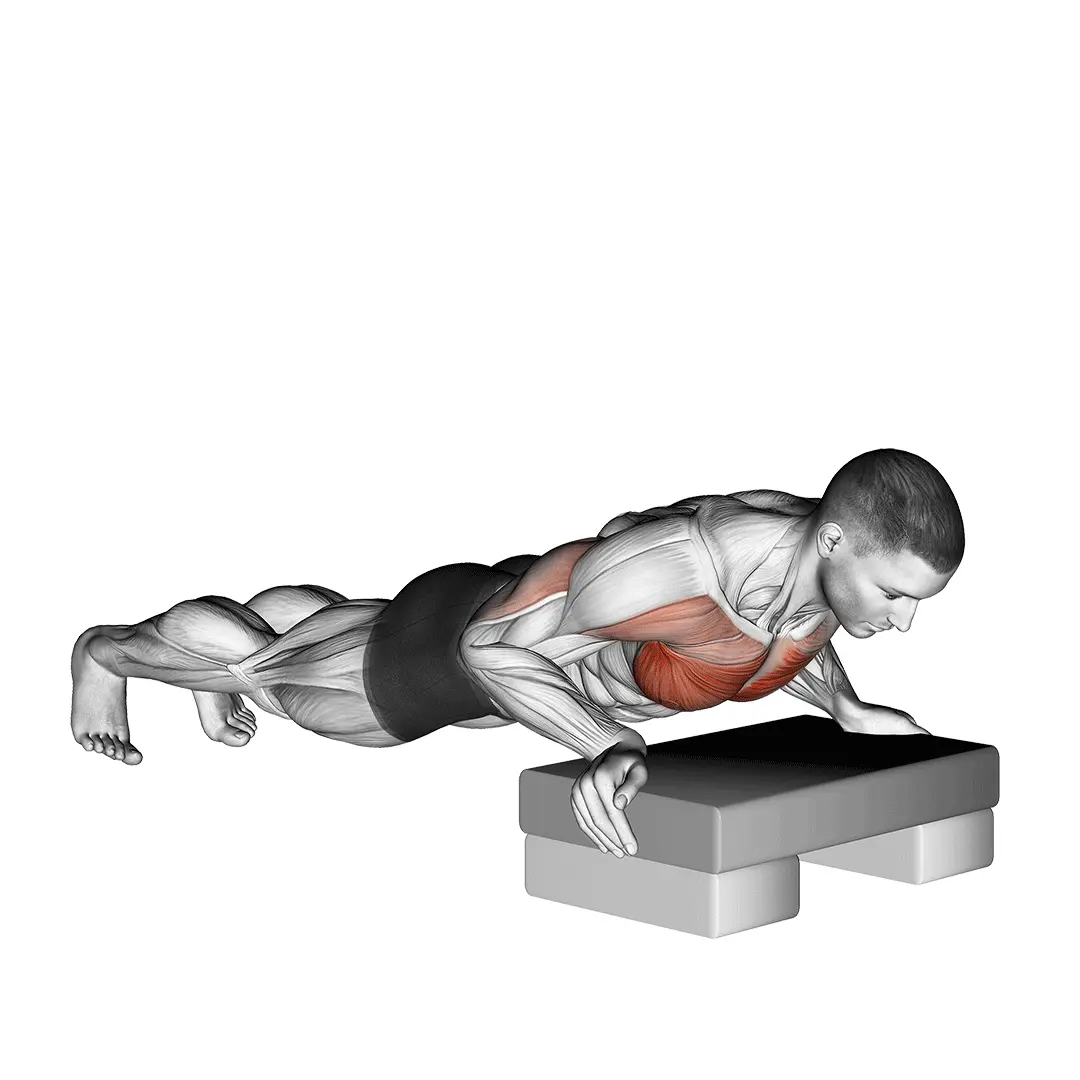
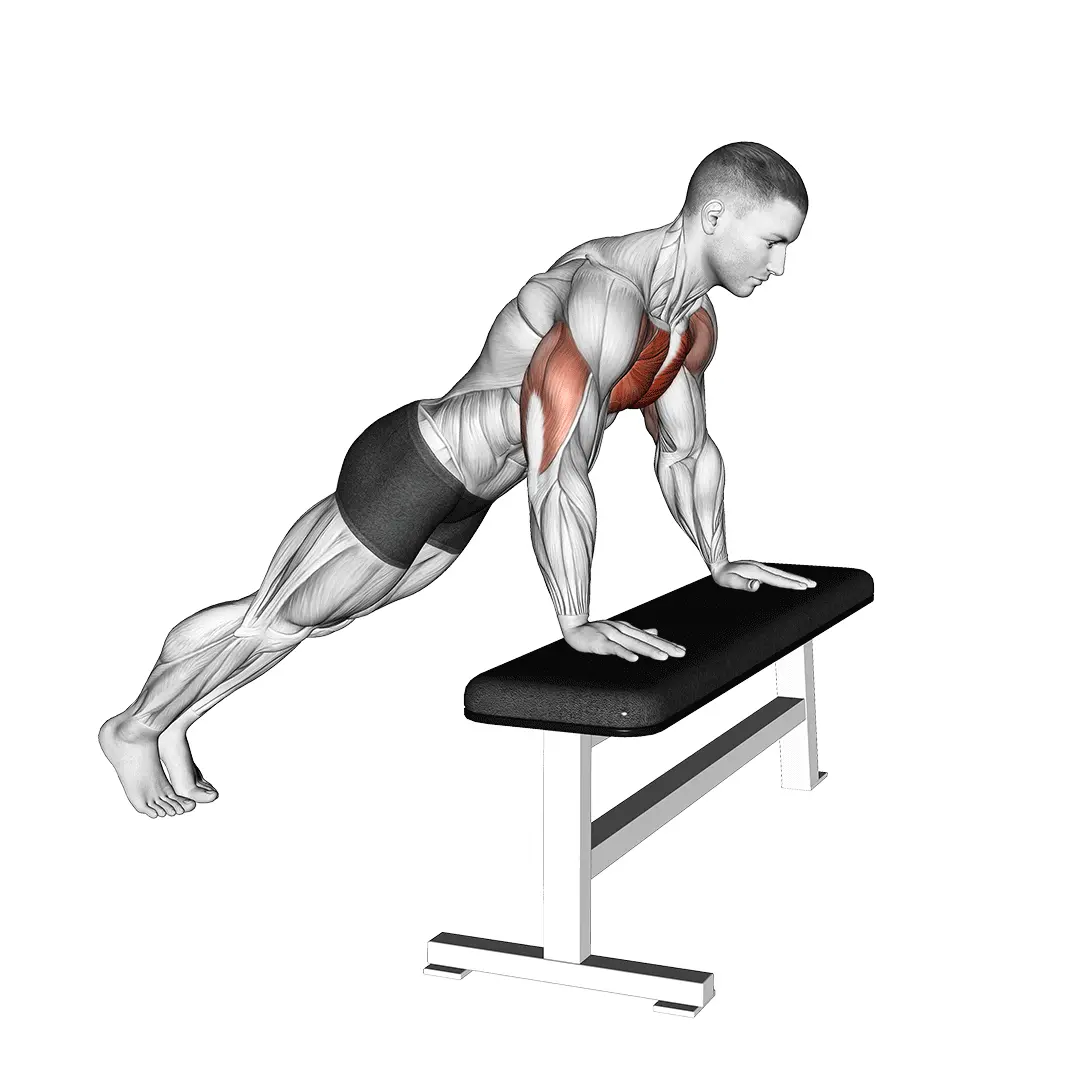
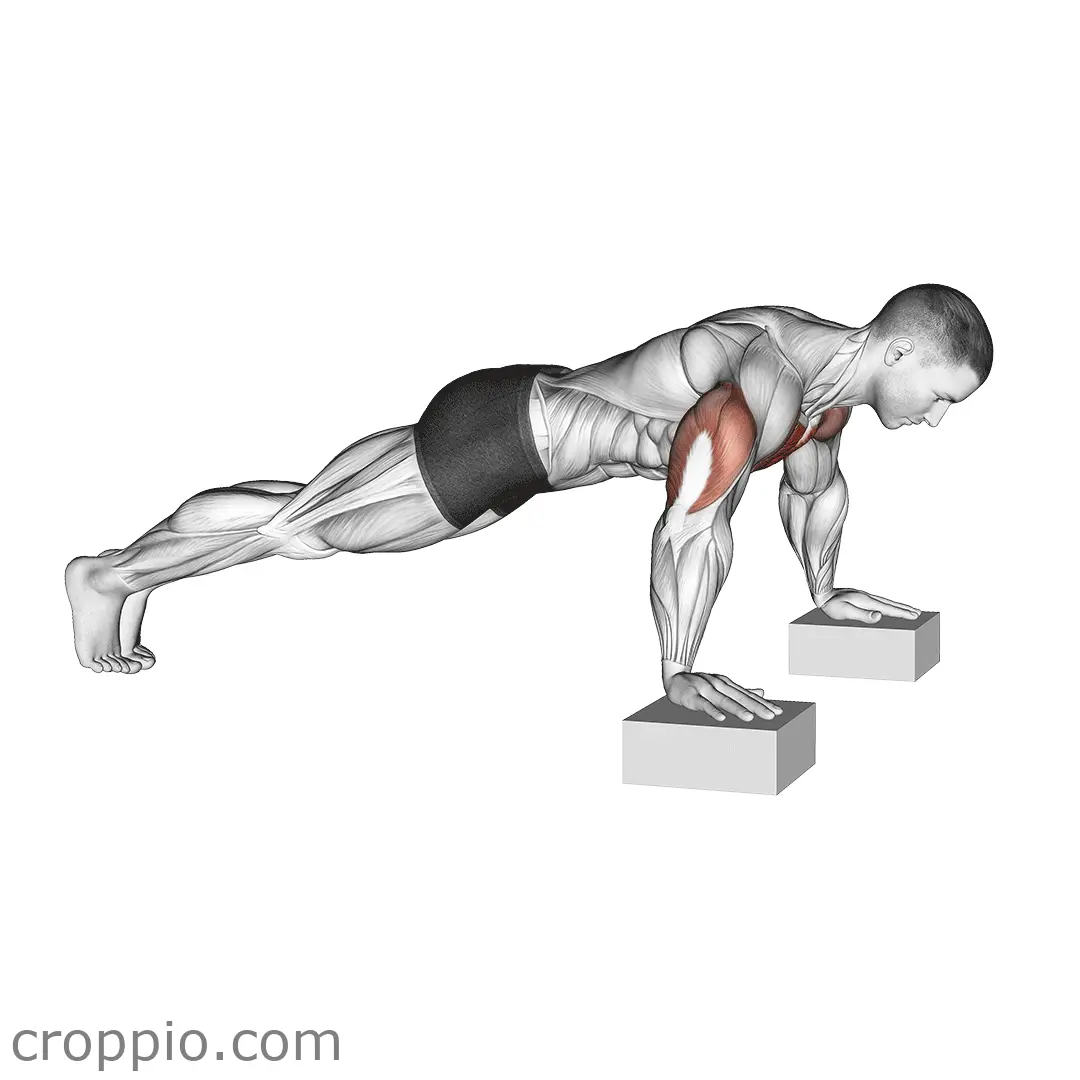
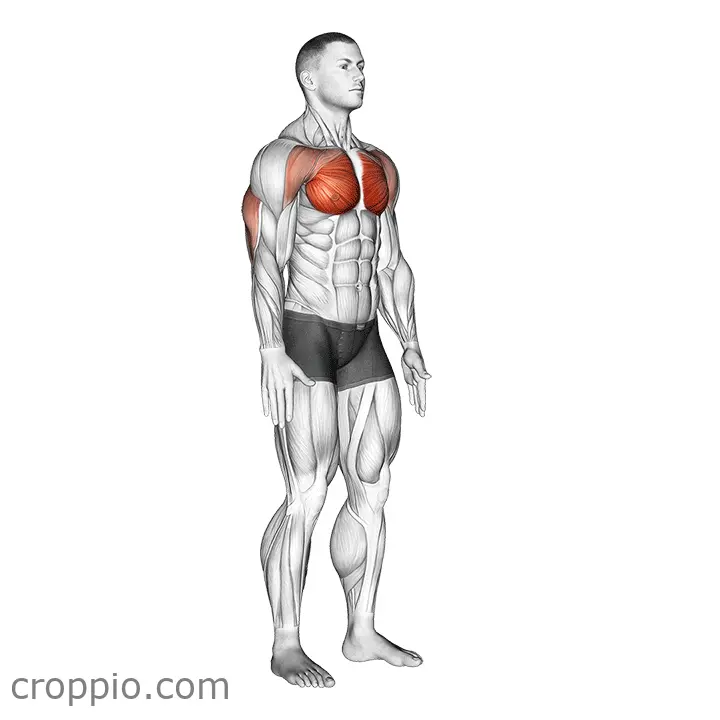
The chest squeeze exercise primarily targets the pectoralis major, which is the large muscle in the chest responsible for pushing movements. Additionally, the pectoralis minor also plays a supportive role in this exercise. Secondary muscles engaged during the chest squeeze include the anterior deltoids in the shoulders and the triceps brachii, which help stabilize and assist in the movement. By engaging these muscles, the chest squeeze not only strengthens the chest area but also contributes to overall upper body stability and power.
Top Mistakes
- Improper hand placement: Ensuring that your hands are aligned correctly will maximize muscle engagement.
- Rushing the movement: Quick repetitions can lead to poor form and decrease the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Neglecting core engagement: Failing to stabilize the core can lead to unnecessary strain on the lower back.
- Excessive weight: Using weights that are too heavy can compromise form and increase the risk of injury.
Execution Tips
- Start with the right equipment: Use a pair of dumbbells or a resistance band for optimal resistance.
- Maintain a neutral spine: Keep your back straight and avoid arching or rounding your spine during the exercise.
- Engage your core: Tighten your abdominal muscles to provide support and maintain a stable position throughout the movement.
- Control the tempo: Perform the squeeze slowly and deliberately, allowing for both contraction and release phases.
- Focus on squeezing: At the peak of the movement, consciously squeeze your chest muscles for maximum contraction.
Workouts
The chest squeeze can be easily incorporated into various workout routines. A suggested format would be three sets of 10-15 reps, ensuring you allow adequate rest (about 60 seconds) between sets. This exercise pairs well with complementary exercises such as push-ups, dumbbell bench presses, and tricep dips, creating a balanced upper body workout. Moreover, you can include this exercise in a circuit training routine, alternating it with lower body exercises for a full-body session.
Conclusion
The chest squeeze is a simple yet effective exercise that strengthens the chest, shoulders, and triceps while enhancing overall upper body stability. Its versatile nature allows for easy adaptation into various workouts, making it a valuable addition to any fitness regimen. By focusing on proper form and technique, individuals can avoid common mistakes and reap the full benefits of this exercise, including improved muscle definition and functional strength.