Barbell Push Jerk Muscles
Similar exercises
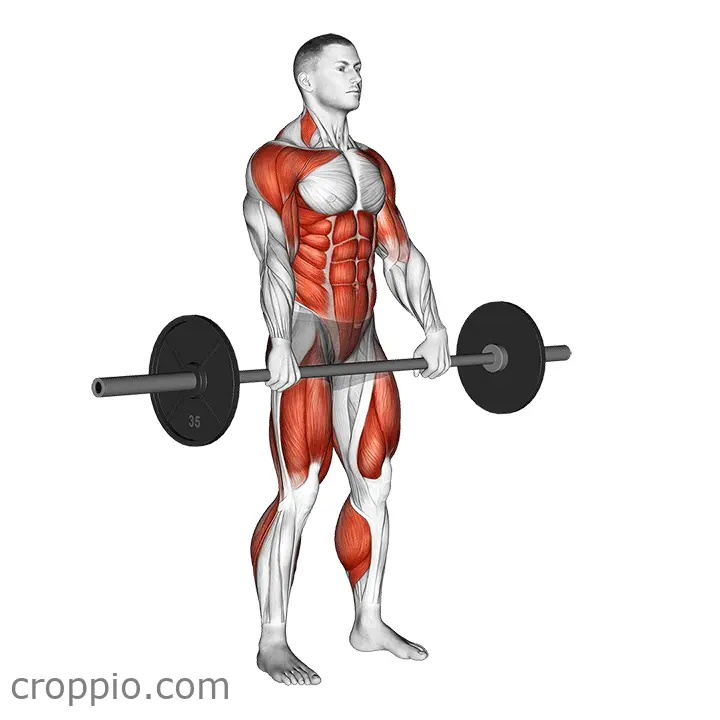
Muscles Involved
The barbell push jerk is a dynamic compound exercise that primarily targets the shoulders and legs, making it an exceptional full-body movement. The primary muscles involved include:
- Deltoids: The anterior, medial, and posterior heads are heavily engaged to stabilize and press the weight overhead.
- Quadriceps: The explosive movement from a squat helps strengthen the quads significantly.
- Glutes: The hip extension contributes to powerful leg drive, engaging the glute muscles intensely.
- Triceps: These muscles assist in locking the arms out during the overhead position.
- Core: The abdominals and obliques work to stabilize the torso throughout the lift.
Additionally, secondary muscles such as the hamstrings and lats come into play to assist in providing stability and strength during the movement.
Top Mistakes
- Improper Foot Placement: Failing to have feet shoulder-width apart may lead to balance issues.
- Not Fully Extending the Arms: Incomplete or rushed extension can result in loss of control and increased risk of injury.
- Using the Back Instead of Legs: Relying on back strength rather than leg drive can lead to poor form and potential injury.
- Inadequate Core Engagement: Neglecting to brace the core leads to instability and ineffective lifting mechanics.
Execution Tips
- Start with Your Feet: Position your feet shoulder-width apart and keep a slight bend in the knees.
- Maintain a Neutral Spine: Keep your back straight and chest up to avoid any strain during the lift.
- Engage Your Core: Tighten your abdominal muscles throughout the movement for stability and support.
- Drive Through Your Heels: Use your legs to generate power as you push the barbell overhead.
- Finish with a Lockout: Ensure your arms are fully extended with the barbell directly over your shoulders and hips.
Workouts
The barbell push jerk can be effectively incorporated into both strength training and conditioning workouts. A recommended structure is:
- 3-4 Sets of 5-8 Reps: Focus on heavier weights to build strength, ensuring proper form is maintained.
- For Conditioning: Perform lighter weights for 3-5 sets of 10-15 reps with shorter rest periods.
- Complementary Exercises: Pair with box jumps, kettlebell swings, or thrusters to enhance functional strength and conditioning.
Conclusion
The barbell push jerk is an exceptional exercise for developing explosive power, overall strength, and coordination. It enhances functional fitness, making it applicable in daily activities and various sports. With its focus on multiple muscle groups, proper execution of this move can lead to significant improvements in athletic performance and physique.