Assisted Dip

Latest Videos
No videos available.
Assisted Dip Workouts
Similar exercises
Muscles Involved
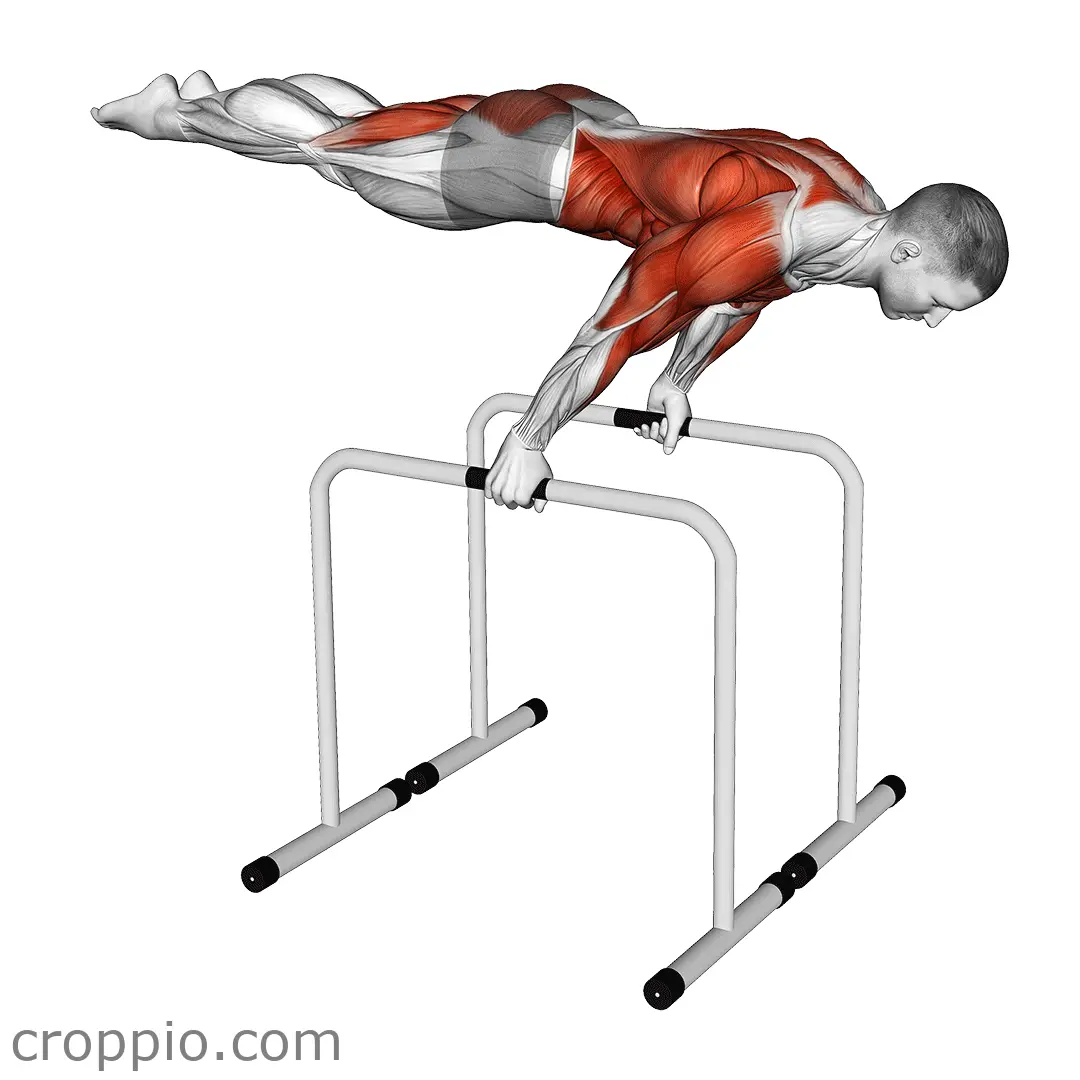
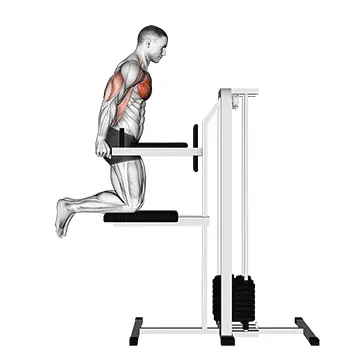
The assisted dip primarily targets the triceps brachii, which is responsible for elbow extension during the movement. Additionally, the exercise engages the pectoralis major and minor, particularly the lower and outer portions, helping to develop the chest. The anterior deltoids (front shoulders) also play a significant role, providing stability throughout the dip. Secondary muscles, including the rhomboids and latissimus dorsi, assist in maintaining proper posture and control while the body performs the dip.
Top Mistakes
- Too Much Body Swing: Using momentum instead of controlled movements can lead to improper muscle engagement and potential injury.
- Allowing Shoulders to Rise: Letting the shoulders elevate towards the ears reduces the effectiveness of the dip and increases stress on the shoulder joints.
- Insufficient Range of Motion: Not lowering the body enough can lead to underdevelopment of the targeted muscles; aim for a 90-degree elbow bend.
- Feet Too Close: Positioning the feet too near can restrict movement and limit muscle activation; always keep them extended for better form.
Execution Tips
- Start by Setting Up: Adjust the machine to accommodate your height, ensuring a stable grip on the handles.
- Engage Your Core: Maintain a tight core throughout the movement to support your upper body and improve overall stability.
- Lower Slowly: Focus on descending in a controlled manner, keeping elbows close to the body, aiming for a 90-degree angle.
- Push Back Up: Exert even pressure on both arms as you push yourself back to the starting position, without locking elbows at the top.
Workouts
Incorporate assisted dips into your workout routine by performing 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 12 reps, adjusting the assistance level according to your strength. Pair assisted dips with complementary exercises such as push-ups, tricep extensions, or bench presses to create a balanced upper body workout. Allow adequate rest intervals of 60 to 90 seconds between sets for optimal recovery and performance.
Conclusion
The assisted dip is a fundamental exercise that significantly enhances upper body strength, focusing on the triceps, chest, and shoulders. By promoting muscle hypertrophy and improving overall functional fitness, it is an excellent addition to any strength training routine. Regular practice can lead to increased muscle definition and endurance, making it a vital exercise for beginners and advanced lifters alike.